Choosing the right HVAC system for your facility or home is about more than comfort; it directly impacts operational costs, equipment uptime, and long-term maintenance budgets. Many decision-makers end up overpaying or choosing systems that are too small simply because they aren’t fully aware of what each system offers.
Understanding how your heating and cooling system works is essential when planning improvements, replacements, or new installations in your home. With the U.S. residential HVAC market projected to grow to USD 31.4 billion by 2034 at a 7.5% CAGR, more homeowners are investing in systems that meet their needs efficiently.
This guide will help you understand the types of HVAC systems available for homes, their key features, and which setups work best for different needs.
Key Highlights:
HVAC systems control heating, cooling, ventilation, and airflow, which directly affect comfort, energy use, and indoor air quality in your home.
Key components like heating and cooling units, ductwork, thermostats, and ventilation work together to keep temperatures consistent and support steady system performance.
Different HVAC types, from split and hybrid systems to ductless mini-splits, hydronic setups, and portable units, provide options based on home size, layout, and specific heating or cooling requirements.
Avoiding common mistakes such as improper sizing, poor ductwork, or DIY installation helps maintain long-term performance, comfort, and system reliability.
What is an HVAC System and Why it Matters for Your Home?
An HVAC(Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system controls how comfortable your home feels throughout the year. It manages heating, cooling, airflow, and humidity, all of which directly affect daily living conditions and energy costs.
Maintains indoor comfort: An HVAC system keeps your home warm in winter and cool in summer, helping maintain steady comfort regardless of outdoor conditions.
Controls energy usage: A properly sized system limits unnecessary energy consumption and helps keep monthly utility bills under control.
Supports indoor air quality: Proper ventilation helps remove dust, allergens, and stale air, improving overall indoor air quality for your household.
Prevents uneven temperatures: The right HVAC setup reduces hot and cold spots, helping keep temperatures balanced throughout the home.
Protects long-term home value: A reliable HVAC system adds to your home’s appeal and reduces costly repairs over time.
When your HVAC system is designed and installed correctly, it supports comfort, cost control, and peace of mind for years to come.
Key Components of HVAC Systems
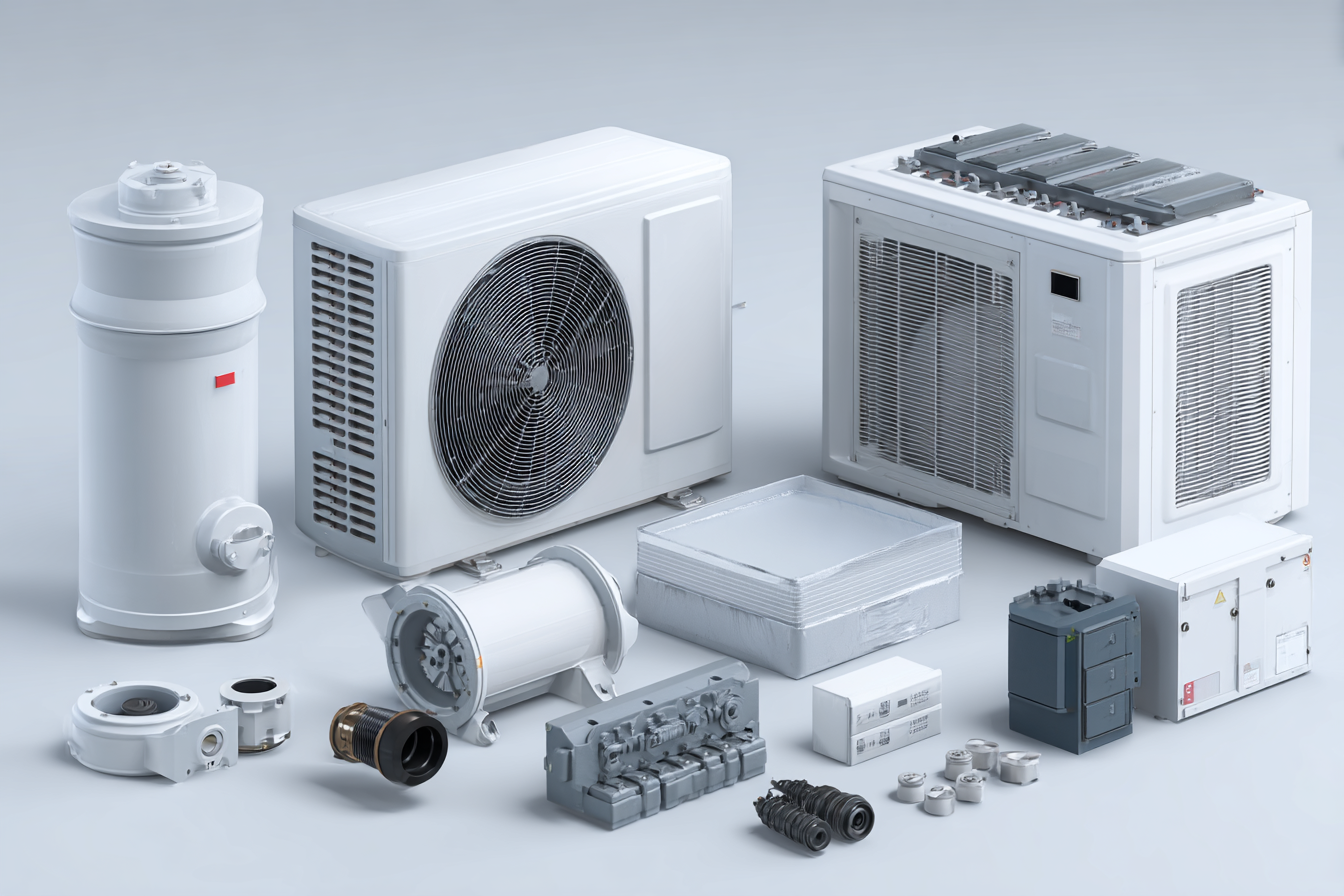

Every HVAC system, regardless of type, relies on several core components to function properly. Understanding these elements helps homeowners better understand how systems operate and where maintenance is needed.
Heating Unit: This component generates warmth during colder months. Common options include gas furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps, each suited to different home layouts and energy needs.
Cooling Unit: The cooling system removes heat from indoor air and releases it outside. Central air conditioners and heat pumps are the most common choices for maintaining consistent indoor cooling.
Ductwork or Air Distribution System: Ducts carry heated or cooled air throughout the home. Well-designed and properly sealed ductwork helps maintain balanced temperatures and reduces unnecessary energy loss.
Thermostat and Controls: The thermostat allows homeowners to set and adjust indoor temperatures. Modern systems often support smart thermostats for better control and more flexible scheduling.
Ventilation Components: These parts manage airflow and support indoor air quality by allowing fresh air circulation and removing stale air.
Each of these parts plays a crucial role in comfort, energy efficiency, and system longevity. Regular maintenance helps all components work together smoothly.
Types of HVAC Systems for Homes

Selecting the right type of HVAC system depends on your home’s size, layout, and heating/cooling needs. Below is a list of the most common HVAC systems used in residential settings.
Split System
A split system is the most common type of HVAC setup in the U.S., separating heating and cooling units. The heating system (furnace or heat pump) is usually placed indoors, while the cooling system (air conditioner) is installed outside.
Key Features:
Separate indoor and outdoor units: This helps with noise reduction and efficient installation.
Uses ductwork: Air is distributed through ducts to all rooms.
Single thermostat control: One control manages both heating and cooling cycles.
Best For: Homes with existing ductwork that need reliable year‑round heating and cooling.
Hybrid Split System
A hybrid split system works much like a traditional split system, but pairs a gas furnace with an electric heat pump. The system automatically switches between fuel sources based on which option costs less at the time.
Key Features:
Dual fuel operation: Uses electricity for mild weather and gas for colder conditions.
Efficient fuel use: Reduces energy usage by choosing the least expensive heat source.
System flexibility: Works well in varying seasonal temperatures.
Best For: Homeowners who want comfort with smarter fuel usage in areas with both cold winters and hot summers.
Packaged Heating and Cooling
Packaged systems house all components, including heating and cooling units, in a single outdoor unit. Air is usually delivered through ducts from the rooftop or outside.
Key Features:
All‑in‑one unit: Eliminates the need for a separate indoor furnace or air handler.
Space saving: Keeps equipment outside, often on a ground pad or roof.
Simplified installation: Fewer components to place inside the home.
Best For: Smaller homes or properties lacking indoor space for a traditional split system.
Zoned System
A zoned HVAC system divides your home into separate zones, each with its own thermostat and control. Dampers inside the ductwork open or close to send air only to areas that need it.
Key Features:
Multiple temperature zones: Customize comfort in different rooms.
Better energy use: Only condition areas that are occupied.
Central control panel: Manages all zones from one interface.
Best For: Larger homes or households with different temperature preferences.
Ductless Mini‑Split System
Ductless mini‑split systems provide heating and cooling without traditional ductwork. Each area or room gets its own indoor air‑handling unit connected to one outdoor compressor.
Key Features:
No ductwork: Saves installation costs when ducts aren’t available.
Individual room control: Each indoor unit can run independently.
Quiet and efficient: Less energy is lost through duct leaks.
Best For: Older homes, additions, or rooms that need supplemental heating and cooling.
Hydronic System
Hydronic HVAC systems use heated or chilled water to move heat to and from living spaces. This system can be paired with radiators, baseboards, or underfloor heating.
Key Features:
Water‑based heating and cooling: Offers smooth, even temperatures.
Radiant floor options: Comfortable underfoot heating.
Durable system components: Often a durable choice.
Best For: Homes with radiant floor systems or those that want quiet, consistent heating.
Portable Spot Cooler
Portable spot coolers are mobile units that provide temporary cooling to specific areas. They are typically used in spaces that are too hot or lack central cooling.
Key Features:
Mobile cooling: Can be moved from one room to another.
Quick setup: No complex installation needed.
Targeted use: Great for hot spots or small spaces.
Best For: Temporary cooling needs or supplemental cooling in specific areas.
Portable Heat Pump
A portable heat pump provides both heating and cooling in a compact, mobile form. Like other heat pumps, it moves heat rather than generating or burning fuel.
Key Features:
Two‑in‑one system: Offers both heating and cooling.
Electric operation: Doesn’t require gas lines or extensive ductwork.
Easy mobility: Can be shifted where comfort is needed.
Best For: Small spaces, temporary living areas, or rooms without duct systems.
Common HVAC Installation and Replacement Mistakes to Avoid
Installing or replacing an HVAC system is a major investment, and small missteps can lead to higher costs and ongoing comfort issues.
Common mistakes include:

Undersized or Oversized Systems: Choosing a system that’s too small or too large leads to uneven temperatures, frequent cycling, and wasted energy.
Skipping Maintenance Considerations: Failing to plan for regular tune-ups shortens system life and increases repair costs over time.
Poor Ductwork Design or Leaks: Incorrect duct sizing or gaps reduce airflow, affect overall system performance, and create hot or cold spots in your home.
Ignoring Energy Efficiency Ratings: Not checking SEER (cooling) or AFUE (heating) ratings can result in higher monthly utility bills.
DIY Installation Risks: Attempting installation without professional guidance can void warranties, lead to errors, and affect system operation.
Overlooking Proper Sizing Calculations: Neglecting load calculations for your home’s square footage, insulation, and climate can result in poor system performance.
Choosing the Cheapest Option: Focusing only on upfront cost may save money initially, but it often leads to higher long-term energy and repair costs.
Avoiding these mistakes ensures your HVAC system delivers comfort, better performance, and reliability for years.
How Quality Comfort Solutions Helps Homeowners Choose the Right HVAC System?
Selecting the right HVAC system can be complex, but Quality Comfort Solutions makes the process simple and reliable. Their licensed team works closely with homeowners to match systems to your home’s needs, energy goals, and comfort preferences. Here’s how they help:
Here’s how we can assist you:
Personalized Home Assessment: The team evaluates your home’s size, insulation, and layout to recommend a system that delivers consistent comfort throughout.
Energy and Cost Guidance: Experts explain energy ratings, operating costs, and potential savings, helping you choose a system that balances comfort and budget.
Tailored System Recommendations: From split systems to ductless mini-splits or heat pumps, they suggest solutions that fit your home and lifestyle.
Professional Installation Services: Certified technicians handle installation with precision, ensuring your HVAC system performs at its best from day one.
Seasonal Maintenance & Tune-Ups: They provide fall and spring maintenance, thermostat calibration, and inspections to keep systems running smoothly year-round.
Prompt, 24/7 Support: Whether it’s a repair, emergency service, or system adjustment, their team is available day or night for peace of mind.
Our approach simplifies the decision-making process, allowing homeowners in Yonkers and Westchester County to invest confidently in a system that suits their unique needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of HVAC systems allows homeowners select a system that improves comfort, reduces energy bills, and increases home value. Choosing a system tailored to your home and lifestyle ensures consistent performance and peace of mind.
Working with a licensed, local provider like Quality Comfort Solutions ensures installation, maintenance, and support are handled with expertise and care. Contact us for a free estimate and find the right system for your lifestyle.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between central HVAC systems and ductless systems?
Central HVAC systems rely on ductwork to circulate air throughout the entire home, providing uniform temperature control. In contrast, ductless systems, also known as mini-splits, deliver conditioned air directly into specific rooms, allowing flexible zoning, higher energy efficiency, and simpler installation in spaces without ducts.
2. How do geothermal HVAC systems function?
Geothermal systems tap into the earth’s relatively constant underground temperature to heat and cool a home. Pipes buried below ground circulate a fluid that exchanges heat with the soil: in winter, the system draws warmth from the ground, and in summer it dumps heat back into it, which can cut energy consumption substantially compared with standard HVAC equipment.
3. When should I consider installing a packaged terminal air conditioner (PTAC)?
PTAC units are ideal for spaces where individual room control is needed, such as hotels, apartments, or offices. Consider them when ductwork isn’t feasible, for energy-efficient localized cooling and heating, or when you want a self-contained system that’s easy to install and maintain.
4. What maintenance is required for different types of HVAC systems?
Maintenance varies: central systems need regular filter changes, duct cleaning, and annual inspections; ductless systems require filter cleaning and occasional professional checkups; geothermal systems need loop inspections and fluid checks; PTAC units need filter cleaning and periodic coil maintenance. Proper care improves efficiency and lifespan.
5. How much does installation cost for various HVAC system types?
Costs depend on system type, home size, and complexity. Central systems range from $3,000–$10,000+, ductless mini-splits $2,000–$7,000 per zone, geothermal systems $10,000–$30,000, and PTAC units $1,500–$4,000 each. Labor, location, and efficiency ratings also influence total installation expenses.