Maintaining a functional heating and air conditioning system is crucial for keeping your home or light commercial space comfortable year-round. Rising energy costs and unpredictable weather make timely repairs more important than ever. A small issue left unchecked can quickly escalate into a major repair, increasing energy bills and reducing system lifespan.
Knowing when repairs are needed and avoiding improper fixes can save time, reduce downtime, and prevent equipment damage. In fact, the HVAC maintenance services market is projected to reach USD 116.57 billion globally by 2030, underscoring the growing reliance on professional repair to maintain efficiency, safety, and reliability.
This blog explores how heating and air conditioning systems are repaired, what you should watch for, and how professional support delivers dependable results.
In a nutshell:
Timely repairs protect system performance, control energy use, and extend the lifespan of heating and air conditioning equipment.
Understanding key components, including heating elements, compressors, ducts, and thermostats, helps you spot issues early and plan repairs effectively.
Common warning signs, such as unusual noises, erratic temperatures, weak airflow, or frequent cycling, indicate when professional intervention is needed.
Proper repair requires the right tools, diagnostic checks, component cleaning, and calibration to keep the system safe, reliable, and performing well.
Following strategic maintenance steps like filter replacement, condenser cleaning, seasonal tune-ups, and performance documentation supports long-term system reliability.
Why You Should Repair Heating and Air Conditioning Systems?
Heating and cooling systems operate under constant mechanical and electrical stress. Over time, even well-maintained equipment develops wear that affects performance and energy use.
Timely repairs can:
Protects system uptime: Addressing worn parts early helps the system run smoothly without sudden shutdowns that disrupt comfort or daily operations.
Controls energy consumption: Faulty components force the system to work harder, raising power usage and monthly energy costs.
Prevents secondary damage: A single unresolved issue can strain connected components, leading to more complex and expensive repairs later.
Maintains consistent indoor temperatures: Repairs correct uneven heating or cooling, keeping your space comfortable and productive.
Extends equipment lifespan: Systems that receive timely repairs experience less wear and last longer.
Reduces emergency repair risk: Proactive repairs lower the chance of breakdowns during extreme weather, when systems are under the most demand.
Supports predictable maintenance planning: Identifying and fixing issues early allows repairs to be scheduled, avoiding rushed decisions or unexpected service calls.
What Components Make Up a Heating & AC System?
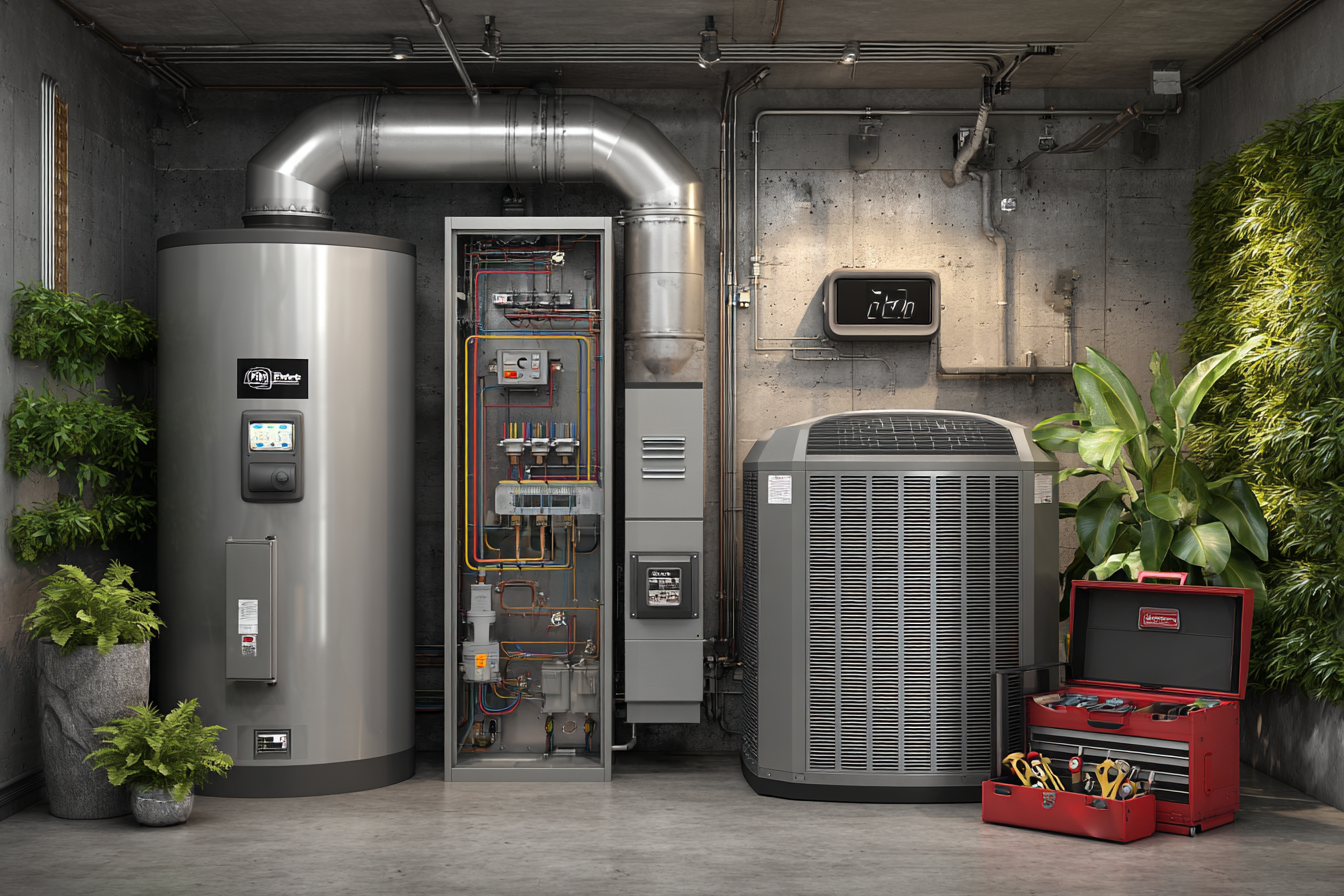

A heating & AC system has several key components, each helping control indoor temperature and airflow. Knowing these parts helps you spot problems early and communicate clearly with your service professional.
Heating system components
Heating systems vary by fuel type, but core components function similarly across furnaces, boilers, and heat pumps.
Key heating components include:
Heat exchanger: Transfers heat into the air without exposing indoor spaces to combustion gases.
Burners or heating elements: Generate heat using gas or electricity.
Blower motor: Pushes heated air through ductwork and into living areas.
Control board: Manages system timing, safety checks, and component communication.
Thermostat: Signals when heating is needed and regulates indoor temperature.
Issues in any of these areas can reduce heat output or create safety concerns.
Air conditioning system components
Cooling systems rely on pressure, airflow, and electrical controls working together. Small disruptions can affect overall performance.
Primary AC components include:
Compressor: Circulates refrigerant and drives the cooling cycle.
Condenser coil: Releases heat from the refrigerant to the outdoor air.
Evaporator coil: Absorbs indoor heat to cool the air.
Refrigerant lines: Move refrigerant between indoor and outdoor units.
Air handler or blower: Distributes cooled air throughout the home.
Proper repairs keep these parts balanced and prevent performance loss.
Ductwork and air distribution
Ductwork delivers conditioned air and plays a major role in overall system performance.
Duct-related issues often involve:
Air ducts: Carry heated or cooled air to different rooms.
Seals and connections: Prevent air loss and pressure imbalance.
Insulation: Helps maintain temperature as air travels through the system.
Repairing ducts keeps comfort consistent and reduces strain on the system.
Recognising these components of a heating and air conditioning system helps you identify potential failure points and determine the scope of repairs.
Common Signs Your Heating & AC System Needs Repair
HVAC systems usually show signs of trouble before a complete breakdown occurs. Below are some of the most frequent indicators that maintenance or repair is needed:
Unusual Sounds or Vibrations: Mechanical rattles, screeches, or clunks often indicate worn bearings, loose parts, or airflow restrictions. Over time, these noises can signal component wear that increases stress on motors or belts.
Erratic Temperature Control: Frequent temperature swings or uneven distribution across spaces suggest airflow imbalances, control sensor faults, or ductwork issues. These conditions can increase cycle times and energy use.
Increased Utility Consumption: A gradual rise in energy use without corresponding outdoor temperature changes often points to system inefficiency. Dirty coils, restricted airflow, or failing compressors are common contributors.
Poor Airflow: Weak airflow at vents can originate from blocked filters, failing blowers, or duct leaks. Reduced airflow lowers delivery capacity and can cause thermal stress on heat exchangers.
Frequent Cycling or Short Runs: Turning on and off too frequently raises wear rates, adds to electrical costs, and may indicate control or sizing issues.
Higher Humidity or Poor Indoor Comfort: Inadequate dehumidification during cooling or dry air during heating can point to system imbalance or thermostat calibration issues.
Each sign affects measurable outcomes such as energy cost per degree of change, equipment runtime balance, and occupant comfort variance. Early recognition helps schedule timely repairs and plan service.
Tools Required for Repairing Heating and Air Conditioning Systems
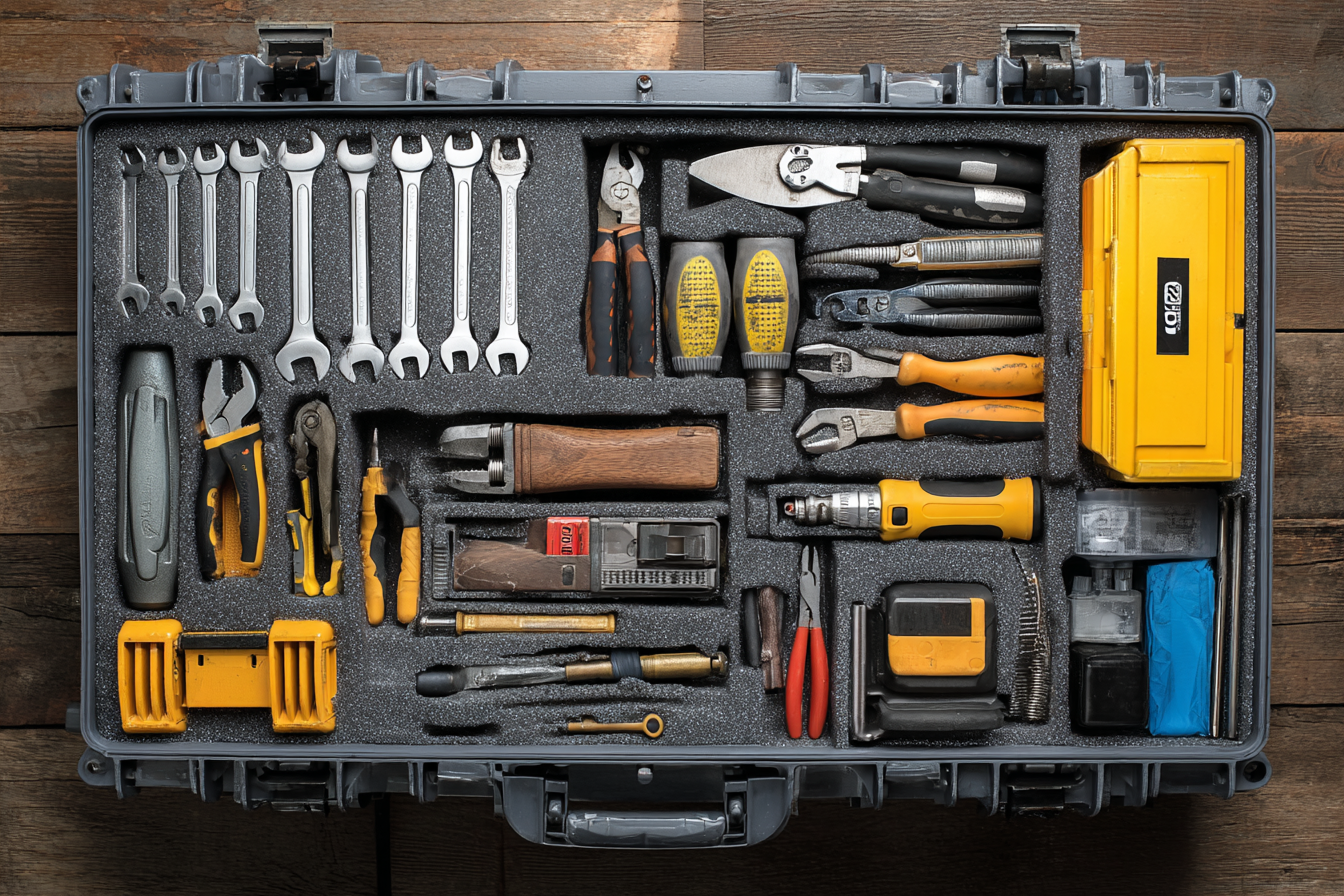

HVAC repairs require specialized tools to ensure safety and effectiveness. While homeowners can identify problems, most repairs are best handled by professionals due to the technical complexity and safety risks.
Common Tools Used:
Diagnostic Tools
Accurate diagnosis depends on precise measurements. HVAC technicians rely on tools that detect issues not visible to the naked eye.
Common diagnostic tools include:
Multimeters: Check electrical continuity, voltage, and component health.
Refrigerant gauges: Measure system pressure to identify cooling performance issues.
Temperature probes: Track heat transfer and confirm proper heating or cooling output.
Airflow measurement devices: Detect airflow restrictions that affect comfort and system load.
These tools help isolate root causes instead of guessing.
Mechanical and Electrical Tools
Heating and cooling systems involve moving parts and electrical circuits. Technicians follow safety and manufacturer standards when performing repairs.
Technicians use:
Insulated hand tools: Protect against electrical hazards during component repairs.
Torque wrenches: Apply correct tension to fittings and connections.
Electrical testing equipment: Verify safe and stable electrical operation after repairs.
Improper handling can create safety hazards or void warranties.
Calibration and Testing Equipment
After repairs, systems must be tested to confirm stable operation.
Equipment includes:
Thermostat calibration tools: Confirm accurate temperature sensing and response.
System testing instruments: Validate airflow, pressure, and electrical stability post-repair.
Performance verification tools: Ensure repairs restore safe, consistent system operation.
Testing verifies that repairs support long-term reliability.
Having the correct tools prevents improper handling, supports accurate diagnosis, and helps ensure that repairs restore system performance without introducing new risks.
Key Strategies for Repairing Heating and Air Conditioning Systems
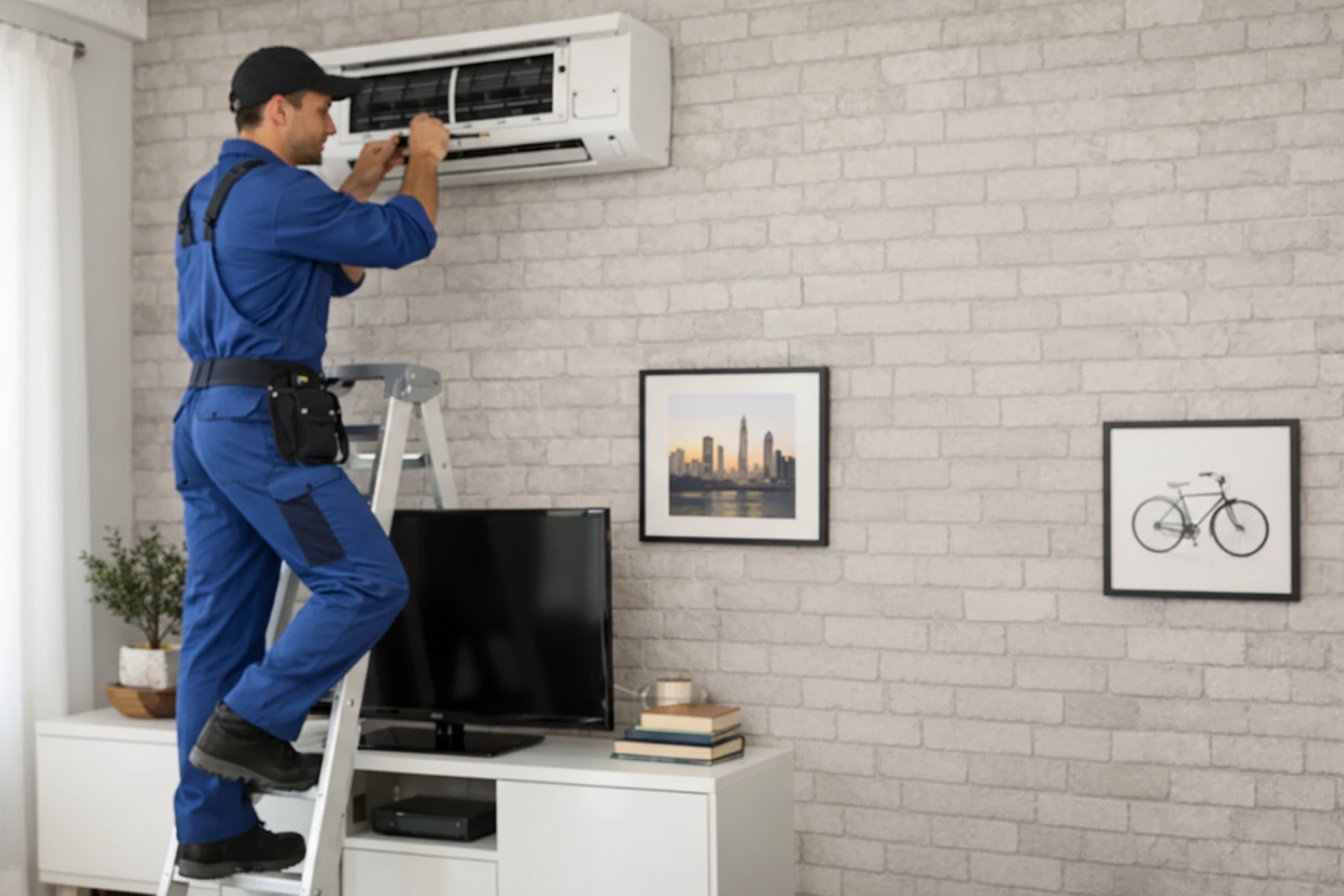

Successful heating and air conditioning systems repair depends on addressing the right issues at the right time. The strategies below focus on prevention and repair planning rather than hands-on work.
Inspect and Replace Air Filters
Air filters directly affect airflow and system load. When filters clog, the system works harder to move air, which increases wear on motors and coils.
Regular filter checks:
Support consistent airflow across rooms
Reduce blower motor and fan stress
Help maintain stable heating and cooling output
Replacing clogged filters on time limits unnecessary system load and prevents premature wear.
Clean Vents, Registers, and Ductwork
Blocked vents and restricted duct paths disrupt air distribution. This often leads to uneven temperatures and longer run times.
Keeping air pathways clear:
Helps balance comfort across rooms
Reduces unnecessary cycling
Helps the system reach set temperatures faster
Professionals should assess ductwork issues beyond visible vents to prevent damage or leaks.
Check and Reset Thermostat Settings
Incorrect thermostat settings can mimic system failure. Programming errors or calibration drift may cause short cycling or inconsistent temperatures.
Thermostat checks help:
Confirm accurate temperature readings
Align system operation with actual demand
Prevent unnecessary heating or cooling calls
Reset or recalibrate settings early to avoid chasing non-existent mechanical issues.
Clear Circuit Breakers and Power Issues
Electrical interruptions are a common cause of sudden system shutdowns. Tripped breakers or loose connections can stop operation without warning.
Before assuming equipment failure:
Check breakers and disconnect switches
Look for repeated trips, not one-time events
Observe whether the system restarts consistently
If breakers trip repeatedly, call a professional to prevent equipment damage.
Clean the Outdoor Condenser Unit
Outdoor units rely on open airflow to release heat. Dirt, leaves, and debris reduce heat transfer and increase operating strain.
Keeping the unit clear:
Supports stable cooling performance
Limits compressor stress
Helps maintain predictable run cycles
Avoid addressing physical damage or coil issues without proper tools and training.
Clear Condensate Drain Lines
Condensate lines remove moisture generated during cooling. When blocked, water can back up into the system or surrounding areas.
Routine checks help:
Prevent water damage and shutdowns
Reduce sensor-triggered system stops
Maintain proper humidity control
Persistent clogs or leaks require professional service to correct alignment or drainage issues.
Test and Clean Coils, Burners, and Sensors
Heat exchange and temperature control depend on clean, responsive components. Dirty coils or sensors cause inaccurate system behavior.
Proper cleaning and testing:
Supports steady heating and cooling cycles
Prevents uneven temperature output
Reduces fuel or electricity waste
These components are sensitive and should be handled carefully to avoid damage.
Inspect Capacitors, Fans, and Refrigerant
Capacitors and fans support the system startup and airflow, while refrigerant enables cooling. Failures in any of these areas reduce system reliability.
Warning signs include:
Delayed startups or humming noises
Weak airflow or inconsistent cooling
Ice buildup or uneven performance
Licensed technicians should handle refrigerant and electrical testing.
Monitor for Refrigerant Leaks and System Performance
Refrigerant loss reduces cooling capacity and increases compressor load. Performance monitoring helps catch these issues early.
Ongoing monitoring helps:
Identify declining performance early
Prevent long-term component damage
Avoid repeat service issues
Report any suspected leak for professional diagnosis and repair.
Schedule Seasonal Tune-Ups
Preventive maintenance aligns system conditions with seasonal demand. Tune-ups help identify wear before it becomes disruptive.
Tune-ups help:
Identify wear before peak usage
Improve system response during extreme weather
Reduce emergency repair risk
Regular service supports smoother operation across heating and cooling seasons.
Document Repairs and Performance Changes
Tracking repairs provides context for future service decisions. It also helps identify patterns that may signal larger issues.
Good documentation:
Supports faster diagnostics
Reduces repeated troubleshooting
Helps plan long-term maintenance
Clear records improve repair accuracy and system reliability over time.
Following these strategies helps improve system performance, minimize downtime, and extend the life of your equipment.
How Quality Comfort Solutions Supports Reliable Heating & AC System Repairs?
Quality Comfort Solutions serves Yonkers and broader Westchester County with licensed HVAC repair support. Our technicians bring years of hands-on experience diagnosing faults that matter to your daily operations, such as airflow imbalance, control faults, or intermittent failures that affect comfort and cost.
Here’s how we can support you:
Licensed, Certified Technicians: Our team brings years of experience to every project, addressing both residential and light commercial HVAC systems.
24/7 Support for Urgent Repairs: We respond promptly to reduce system downtime and restore comfort quickly.
Local Knowledge: Serving Yonkers and Westchester County, we understand regional climate demands and energy concerns.
Comprehensive Service: From routine maintenance to full system repair, we address issues across heating, cooling, and ductwork systems.
System Optimization During Repairs: Repairs include calibration and component checks to ensure that systems operate as reliably as possible post-service.
Professional expertise ensures that repairs are completed safely, efficiently, and in a way that minimizes future problems.
Conclusion
Regular repair and maintenance of heating and air conditioning systems are essential for consistent comfort, energy efficiency, and equipment longevity. Recognizing early warning signs and addressing issues with the right tools and professional guidance can make a measurable difference in performance and cost management.
Combining basic awareness with professional servicing ensures your system operates reliably throughout the year. Quality Comfort Solutions offers licensed, experienced technicians who respond promptly and support system longevity for residents and businesses in Yonkers and across Westchester County.
For support with a repair assessment or to schedule a service visit, contact us for a free estimate.
FAQs
Is it safe to repair my heating or AC system myself?
DIY repairs can be risky due to electrical components, refrigerants, and gas connections. Minor tasks like changing filters are safe, but for complex issues, hiring a licensed technician ensures safety, prevents further damage, and keeps warranties valid.
How can I fix a furnace that won't turn on?
Check the thermostat settings, power supply, and circuit breakers first. Ensure the pilot light or ignition system is working. If the furnace still won’t start, call a certified HVAC technician to inspect components safely and prevent potential hazards.
What should I do if my AC is leaking water?
Turn off the unit and inspect the drain line for clogs. Check for a frozen evaporator coil or low refrigerant levels. While some fixes like clearing a drain line can be DIY, persistent leaks require professional inspection to prevent water damage and system issues.
How often should I perform maintenance on my heating system?
Professional maintenance is recommended at least once a year, ideally before the heating season. Regular checks, filter replacements, and cleaning help improve efficiency, prevent breakdowns, extend system life, and reduce energy bills.
Is my heater blowing cold air instead of warm?
Cold airflow can result from thermostat issues, dirty filters, closed vents, or a malfunctioning pilot/ignition system. Refrigerant or airflow problems may also be involved. A certified technician can accurately diagnose and repair the issue safely.