Maintaining your HVAC system goes beyond comfort; it directly impacts energy costs, equipment reliability, and operational efficiency. Rising energy prices, increasingly complex HVAC systems, and environmental considerations make preventive maintenance an essential part of responsible facility management.
Regular maintenance helps reduce unexpected breakdowns, extend the lifespan of your equipment, improve system performance, and manage energy consumption effectively. In fact, the global HVAC market is projected to reach USD 290.08 billion by 2034, growing at a 5.90% CAGR, reflecting the rising demand for efficient, well-maintained systems.
Following a disciplined maintenance approach can help control operating costs while maintaining safe, predictable indoor environments. This guide walks you through the essentials of HVAC preventive maintenance, outlines strategies to keep your system in good condition, and provides a comprehensive checklist to help you stay on track.
At a Glance:
HVAC preventive maintenance keeps systems reliable and efficient, reduces unexpected breakdowns, and extends equipment lifespan.
Understanding and maintaining core components such as filters, coils, ducts, thermostats, and electrical systems helps ensure strong system performance.
Following strategic maintenance practices, including seasonal tune-ups, performance monitoring, recordkeeping, and professional inspections, helps avoid costly issues.
Using a structured checklist for monthly, seasonal, and annual tasks helps detect problems early and supports consistent energy performance.
Regular maintenance helps prevent common HVAC problems such as restricted airflow, uneven temperatures, refrigerant leaks, electrical failures, and premature component wear.
What is HVAC Preventive Maintenance and Why Is It Important?ce and Why It’s Important?
Preventive maintenance involves planned, routine HVAC inspections and servicing performed before failures occur. The goal is to keep systems operating within expected performance ranges rather than reacting to breakdowns after they disrupt comfort or operations.
Why it matters:
Improves equipment uptime: Well-maintained systems are less likely to fail during peak heating or cooling demand, reducing unexpected downtime.
Supports consistent comfort: Stable airflow and accurate temperature control prevent hot or cold spots that strain equipment and frustrate occupants.
Helps manage energy usage: Clean components and properly adjusted controls reduce wasted energy caused by system inefficiencies.
Extends system lifespan: Reducing stress on key components helps delay major replacements and protects long-term capital investments.
Reduces emergency service calls: Addressing minor issues early lowers the risk of after-hours repairs and urgent service disruptions.
Scheduling routine inspections, cleanings, and adjustments is key to sustaining HVAC performance and reliability throughout the year.
Key Components of an HVAC System to Maintain
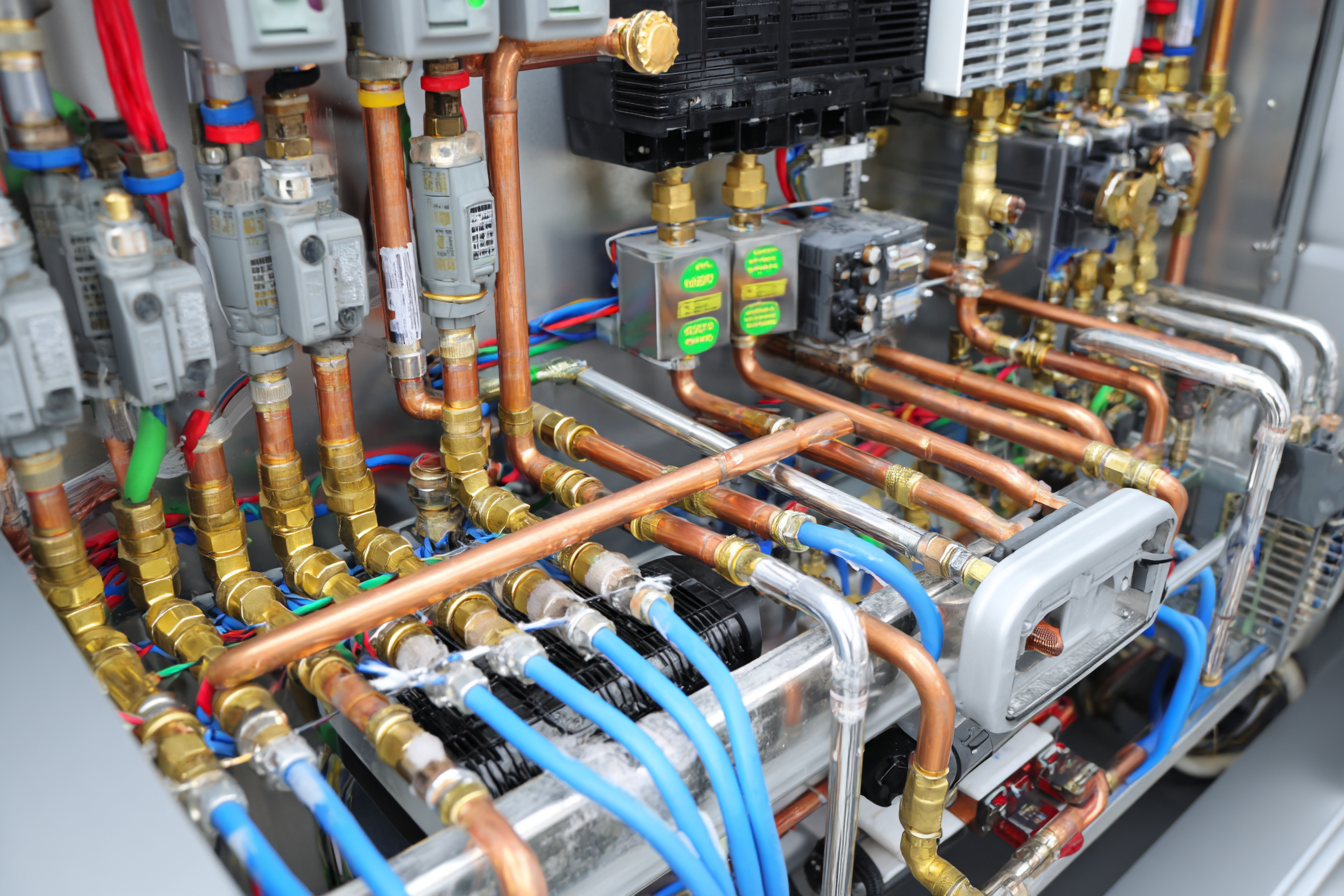
HVAC systems comprise several interacting components that influence system performance and reliability. Understanding each part’s role helps you create a maintenance schedule that protects system uptime and reduces total lifecycle costs.
Core system areas to inspect and maintain:
Air Filters: Air filters capture dust, allergens, and debris. A clogged filter reduces airflow, increases energy consumption, and adds extra strain to the system.
Coils: Both evaporator and condenser coils need cleaning to support proper heat transfer. Dirty coils can cause higher energy usage and uneven heating or cooling.
Ductwork: Properly maintained ducts help keep airflow balanced throughout the home or facility. Leaks or blockages can lead to uneven temperatures and higher energy costs.
Thermostat: Thermostats control the system’s operation. Calibration and inspection help limit temperature fluctuations and reduce unnecessary energy use.
Condensate Drains: Blocked drains can cause water damage or system shutdowns. Regular checks help reduce leaks and moisture-related problems.
Electrical Components: Wiring, connections, and motors should be inspected for wear or corrosion to lower the risk of system failures or safety hazards.
Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can reduce cooling efficiency, increase energy consumption, and potentially damage the compressor.
Blower and Fan Systems: Keeping the blower clean and operating correctly helps maintain proper airflow, reducing strain on the system and preventing uneven heating or cooling.
Maintaining these components limits wear that leads to costly repairs and premature equipment replacement.
Best Strategies for HVAC Preventive Maintenance
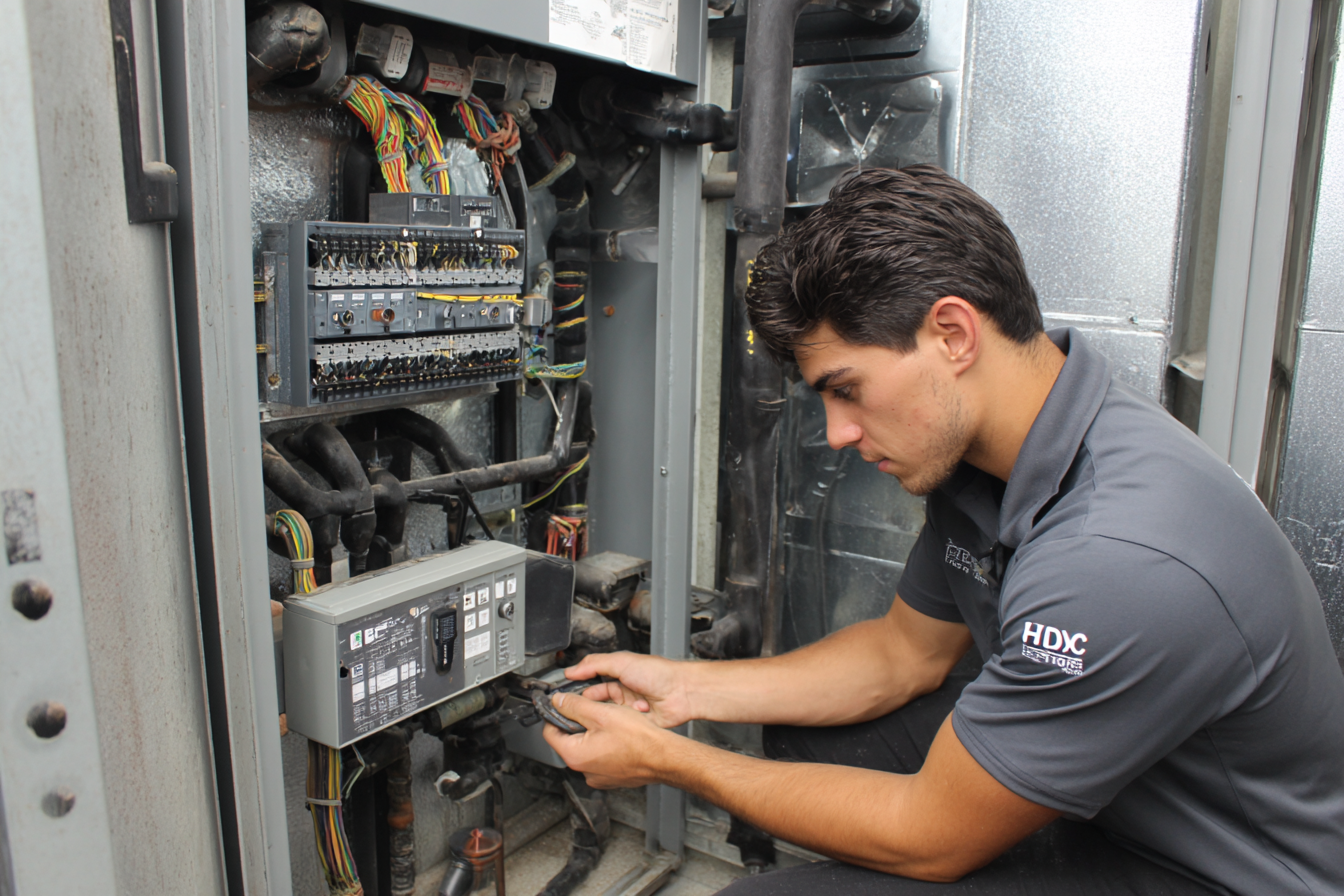

Preventive maintenance is most effective when approached systematically. The strategies below focus on consistency, visibility into system health, and early issue detection.
Schedule Maintenance Around Seasonal Demand
HVAC systems face the most stress during peak heating and cooling seasons. Planning maintenance before these periods helps reduce the risk of failures when systems are operating at maximum load.
Pre-season inspections: Identify worn components before winter heating or summer cooling demand increases.
Load readiness checks: Confirm airflow, electrical connections, and controls can handle extended runtime.
Reduced emergency calls: Early checks help avoid last-minute breakdowns during extreme weather.
Planning around seasons supports stable system operation when comfort and reliability matter most.
Monitor System Performance Indicators Regularly
HVAC issues often show early warning signs before a failure occurs. Monitoring performance indicators allows problems to be addressed while they are still manageable.
Runtime patterns: Longer or irregular run cycles can indicate airflow restrictions or control issues.
Temperature consistency: Uneven heating or cooling across zones may point to duct or balance problems.
Noise and vibration changes: New sounds often signal wear in motors, fans, or mounting components.
Tracking these indicators supports informed maintenance decisions and prevents small issues from escalating.
Maintain Clear and Updated Service Records
Accurate maintenance records provide visibility into system history and help guide future decisions. Without documentation, recurring issues are harder to identify and address.
Service history tracking: Log inspections, part replacements, and corrective actions for reference.
Recurring issue identification: Patterns in repairs can indicate components nearing the end of life.
Informed budgeting: Maintenance data supports better planning for repairs or system upgrades.
Consistent recordkeeping improves accountability and supports long-term system planning.
Perform Focused Seasonal Tune-Ups
Seasonal tune-ups address system-specific needs rather than applying the same checks year-round. This keeps maintenance relevant and cost-effective.
Airflow-related components: Inspect filters, blowers, and duct connections for restrictions.
Heat exchange surfaces: Check coils for dirt buildup that can affect temperature transfer.Electrical connections: Look for loose terminals or worn wiring that could cause shutdowns.
Targeted tune-ups help systems perform consistently during high-demand periods.
Involve Licensed HVAC Professionals for Critical Tasks
Some issues are not visible without proper tools or technical training. Professional involvement helps reduce risk and improve system reliability.
Electrical and refrigerant handling: Licensed technicians safely inspect and adjust regulated components.
System calibration: Professional tuning ensures the system operates within manufacturer guidelines.
Code and safety compliance: Certified inspections help identify safety risks before they cause failures.
Professional inspections add a layer of protection that routine checks cannot replace.
Align Maintenance Frequency with System Age and Usage
Not all HVAC systems require the same level of attention. Maintenance frequency should reflect how hard the system works and its stage in the lifecycle.
Older systems: Require more frequent inspections due to wear and component fatigue.
High-usage environments: Systems running longer hours need tighter inspection intervals.
Recently installed systems: Benefit from early performance checks to confirm proper installation.
Adjusting maintenance schedules based on usage and age helps control costs while maintaining reliability.
These strategies, when followed consistently, reduce downtime, improve system output, and help maintain predictable energy costs.
Complete HVAC Preventive Maintenance Checklist
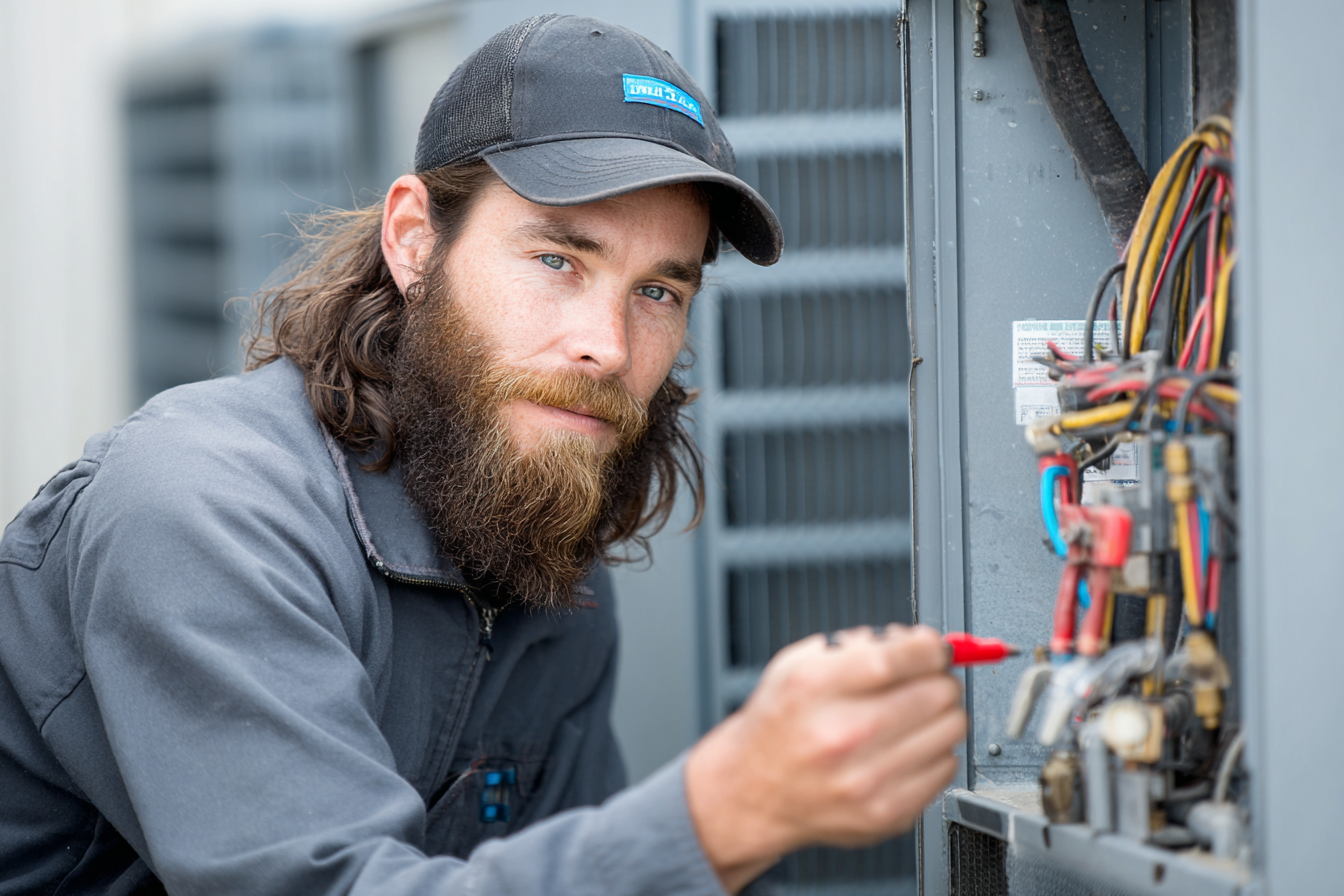

A structured checklist ensures that all crucial components are inspected and maintained consistently. Use the following checklist for a comprehensive preventive maintenance routine:
Seasonal Maintenance (Fall & Spring)
Seasonal maintenance prepares HVAC systems for high-demand periods. Fall and spring inspections help catch wear from the previous season and reduce the risk of breakdowns when heating or cooling loads increase.
System Area | Maintenance Task | Why It Matters |
Heating Equipment | Inspect burners, heat exchangers, and ignition components | Helps prevent uneven heating, system shutdowns, and safety risks |
Boilers | Check pressure levels, valves, and circulating pumps | Supports stable heat output and avoids unexpected pressure faults |
Heat Pumps | Inspect reversing valves and defrost controls | Maintains reliable heating and cooling transitions |
Cooling Equipment | Clean condenser and evaporator coils | Improves heat transfer and controls energy consumption |
Refrigerant System | Check refrigerant levels and connections | Prevents cooling loss and compressor strain |
Airflow Components | Inspect blowers and fan motors | Supports consistent airflow and reduces motor wear |
Ductwork | Inspect visible ducts for leaks or insulation damage | Reduces energy loss and uneven temperature distribution |
Drainage | Clear condensate drains and pans | Prevents water damage and humidity-related issues |
Controls | Test thermostat accuracy and system response | Supports stable temperature control and avoids short cycling |
Electrical | Tighten connections and inspect contactors | Reduces risk of electrical failure during peak operation |
Monthly or Quarterly Checks
Monthly or quarterly checks focus on early detection. These tasks are lighter than seasonal maintenance but play a critical role in identifying airflow restrictions, control issues, and performance drift before they escalate.
System Area | Maintenance Task | Why It Matters |
Air Filters | Inspect and replace if needed | Maintains airflow and reduces strain on fans and coils |
Thermostat | Verify settings and calibration | Helps maintain consistent indoor conditions |
Condensate Lines | Inspect for blockages or leaks | Prevents moisture buildup and system shutdowns |
Outdoor Units | Check for debris around condensers | Maintains proper airflow and heat rejection |
Electrical Components | Visual inspection of wiring and connections | Helps identify early signs of wear or overheating |
System Operation | Listen for unusual noise or vibration | Early indicator of mechanical or motor issues |
Energy Use | Review recent utility usage patterns | Flags performance changes that may require inspection |
Safety Controls | Test limit switches and shut-off functions | Supports safe operation and compliance |
Annual or Biannual Checks
Annual or biannual inspections focus on deeper system health. These checks support long-term planning, helping decision-makers assess repair vs. replacement timelines and budget more accurately.
System Area | Maintenance Task | Why It Matters |
Heat Exchangers | Detailed inspection for cracks or corrosion | Reduces safety risks and heating failure |
Compressors | Evaluate performance and electrical load | Helps prevent costly compressor breakdowns |
Motors & Bearings | Lubricate and assess wear | Extends component life and reduces friction losses |
Refrigerant System | Full leak detection and performance review | Supports stable cooling and protects major components |
Ductwork | Inspect overall airflow balance | Improves comfort, consistency, and system performance |
Controls & Sensors | Recalibrate temperature and pressure sensors | Supports accurate system control |
System Performance | Review maintenance history and repair trends | Helps plan replacements and budget accurately |
Professional Assessment | Schedule a licensed HVAC inspection | Provides expert insight into system condition and risks |
Tip: Use this checklist regularly and maintain records for each completed task. It helps identify patterns that can improve uptime and reduce repair costs over time.
Common HVAC Problems Preventable with Regular Maintenance
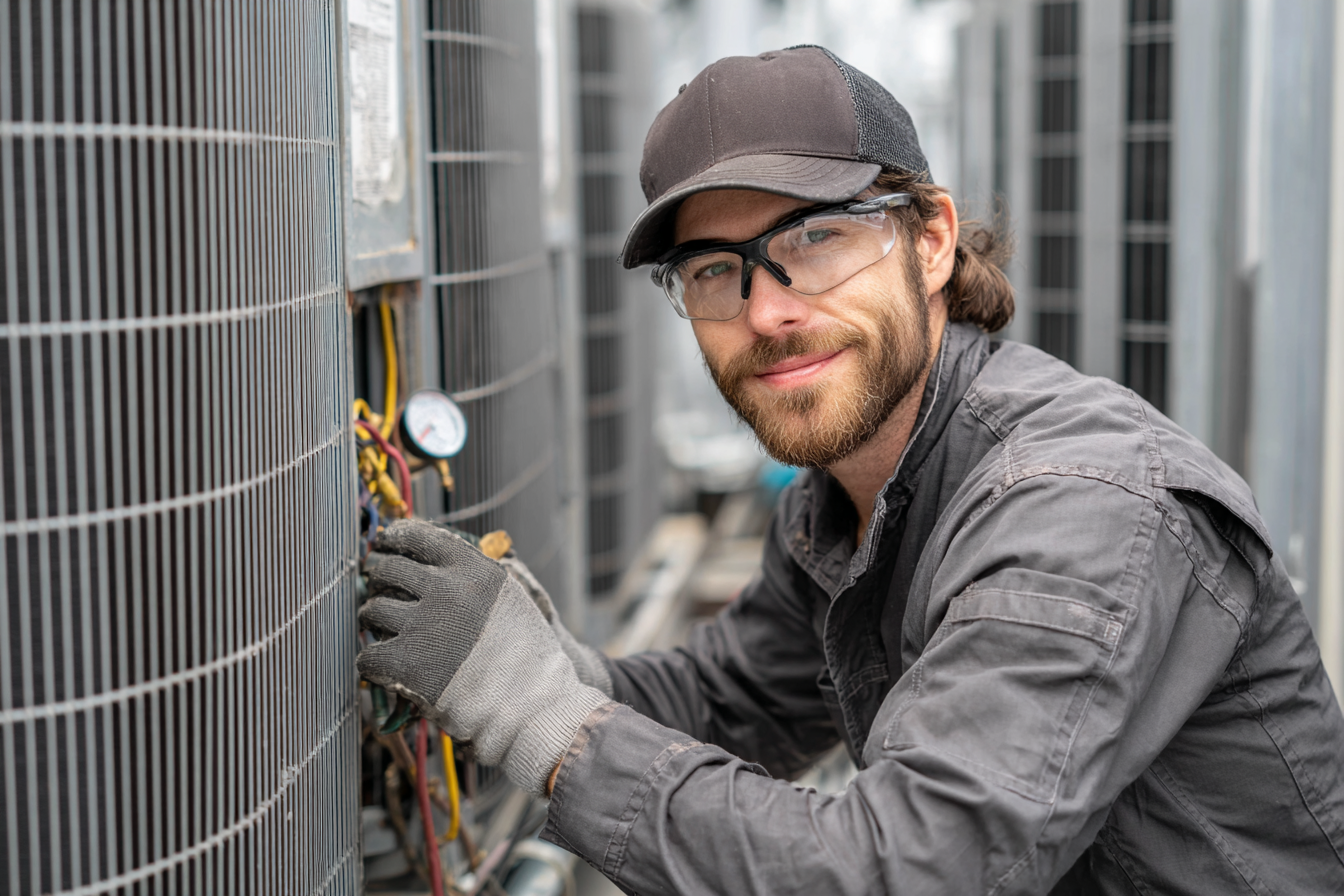

Many costly HVAC issues can be avoided with a structured preventive maintenance program. Understanding these common problems helps prioritize tasks and protect operations.
Restricted airflow: Dirty filters, clogged coils, or blocked ducts limit airflow, forcing the system to work harder and increasing wear on key components.
Uneven heating or cooling: Poor airflow, duct leaks, or thermostat issues can cause hot and cold spots, leading to comfort complaints and inconsistent system output.
Refrigerant-related issues: Low or leaking refrigerant reduces cooling capacity and puts extra strain on the compressor, increasing the risk of major repairs.
Electrical failures: Loose connections or aging wiring can trigger unexpected shutdowns and pose safety risks if left unaddressed.
Thermostat inaccuracies: Miscalibrated thermostats cause frequent cycling and temperature swings, leading to unnecessary energy use and system stress.
Water leaks and moisture buildup: Clogged condensate drains can cause leaks, water damage, and mold growth around HVAC equipment.
Premature component wear: Lack of lubrication, dirt buildup, and unchecked vibration accelerate wear on motors, fans, and bearings.
By addressing these issues proactively, you improve equipment reliability and support measurable operational KPIs, such as uptime, throughput, and energy cost management.
How Quality Comfort Solutions Can Support Your HVAC Maintenance Needs?
Maintaining HVAC systems requires both planning and execution. Quality Comfort Solutions brings local expertise and licensed technicians to support your facility’s maintenance goals throughout Westchester County.
Here’s how we can assist you:
Licensed Experts: Certified technicians provide comprehensive inspections, repairs, and system calibrations.
Scheduled Preventive Maintenance: Customized plans for fall, spring, or year-round services reduce downtime and support energy efficiency.
Component-Specific Services: From boilers and furnaces to central AC and heat pumps, all key systems are covered.
Documentation and Reporting: Clear service records help facility managers track performance, budget maintenance, and plan replacements.
24/7 Support: Prompt responses to urgent issues minimize disruption and ensure uninterrupted comfort.
By leveraging professional expertise, property owners and facility managers can implement a structured maintenance plan to ensure their HVAC systems run efficiently and reliably year-round.
Conclusion
Preventive HVAC maintenance is a critical investment in comfort, reliability, and energy management. By implementing a structured maintenance program, using a detailed checklist, and addressing issues proactively, you can significantly reduce downtime, manage energy costs, and extend the life of HVAC equipment.
Professional support from a licensed provider like Quality Comfort Solutions ensures maintenance is thorough, timely, and tailored to your system’s needs. Their expertise in heating, cooling, ductwork, and controls supports consistent comfort and operational efficiency.
Contact us for a free estimate and get practical guidance on maintaining reliable, cost-controlled heating and cooling for your space.
FAQs
How often should I perform preventive maintenance on my HVAC system?
You should perform preventive HVAC maintenance at least twice a year—once before the cooling season and once before the heating season. Regular inspections help improve efficiency, reduce unexpected breakdowns, extend equipment lifespan, and ensure consistent indoor comfort.
What tools do I need for basic HVAC preventivemaintenance?
Basic HVAC preventive maintenance typically requires simple tools such as a screwdriver set, a multimeter, a vacuum or shop vac, coil cleaner, a fin comb, a soft brush, a thermostat thermometer, and replacement air filters for routine cleaning and inspection.
How can I inspect and clean HVAC coils as part of the checklist?
Start by turning off the unit's power. Visually inspect coils for dirt, dust, or corrosion. Gently brush loose debris, then apply an approved coil cleaner. Rinse carefully, if required, and allow the coils to dry before restoring power.
What are the signs that my HVAC system needs immediate maintenance?
Common signs include unusual noises, weak airflow, inconsistent temperatures, rising energy bills, frequent cycling, unpleasant odours, or visible leaks. If your system struggles to maintain comfort or suddenly performs poorly, immediate professional maintenance is recommended.
How do I test and maintain the accuracy of an HVAC thermostat?
Test thermostat accuracy by comparing its reading with a reliable room thermometer. If temperatures differ, recalibrate or replace the thermostat. Keep it clean, free from dust, and away from heat sources to ensure accurate readings and efficient system operation.