Keeping your facility or home comfortable depends on a reliable air conditioning system, but even the best units lose efficiency when maintenance is overlooked. Equipment breakdowns, inconsistent cooling, and rising energy bills can disrupt daily operations, increase maintenance costs, and put pressure on your team to resolve issues quickly.
Regular maintenance reduces these risks and keeps your indoor climate reliable. By addressing common issues early, you can improve system performance, extend equipment lifespan, and lower operational costs.
In fact, the U.S. Department of Energy notes that proper AC maintenance can save organizations 5–20% on annual energy bills. A well-maintained system also ensures consistent air quality, creating a safer, more comfortable environment for employees, clients, and visitors alike.
This guide provides practical strategies to help you maintain your AC system, understand its components, and recognize common problems.
Key Highlights:
Regular maintenance keeps your AC system efficient, extends its lifespan, and ensures consistent cooling and air quality.
Understanding key components like compressors, coils, filters, ducts, and thermostats helps identify potential issues early.
Different AC system types; central air, ductless mini-splits, heat pumps, and window/portable units, require tailored maintenance approaches.
Routine tasks such as inspections, filter changes, coil cleaning, refrigerant checks, and electrical and mechanical maintenance help prevent common problems.
Professional support provides thorough servicing, safe operation, better energy use, and prompt resolution of issues.
Why Maintenance of the Air Conditioning System Is Important?

Air conditioning systems are complex machines with multiple components working together to regulate indoor temperature and air quality. Over time, wear, dirt, vibration, and changing environmental conditions can degrade performance.
Proper maintenance affects these outcomes:
Supports consistent cooling performance: Regular checks help the system maintain stable airflow and temperature control, avoiding hot spots or uneven cooling across rooms.
Reduces unexpected system downtime: Identifying worn components early helps prevent sudden breakdowns during peak summer demand when repairs are more disruptive.
Controls energy consumption over time: Clean components and proper calibration allow the system to operate without unnecessary strain, helping manage monthly energy bills.
Extends overall system lifespan: Routine servicing reduces wear on critical parts like compressors and fans, delaying the need for full system replacement.
Improves indoor air quality: Filter and coil maintenance limits dust, allergens, and moisture buildup that can circulate through indoor spaces.
Protects long-term maintenance budgets: Scheduling maintenance is easier to manage financially than handling emergency repairs caused by neglected components.
Supports safe system operation: Electrical checks and refrigerant inspections help reduce safety risks linked to overheating, leaks, or faulty connections.
Key Components of an AC System
Understanding your AC system’s core components is the first step in effective maintenance. These elements work together to regulate temperature and airflow.
Typical components include:
Compressor: Moves refrigerant through the system to transfer heat. If it works under strain due to poor maintenance, cooling capacity drops and repair costs increase.
Condenser Coil: Releases heat absorbed from indoors to the outside air. Dirt or debris on the coil raises energy use and can cause the system to shut down during peak demand.
Evaporator Coil: Absorbs heat from indoor air. When coils are dirty or frozen, airflow drops and indoor comfort becomes uneven.
Air Filters: Capture dust, pollen, and debris before air circulates. Clogged filters restrict airflow and increase wear on key components.
Ductwork: Distributes cooled air across the building. Leaks or blockages reduce cooling consistency and raise operating costs.
Thermostat: Controls system cycles and temperature settings. Poor calibration leads to unnecessary run time and higher energy bills.
Each of these elements has a measurable impact on KPIs like energy use per cooling ton, fan power draw, and control stability. If any component is degraded, the system has to work harder to achieve set points, driving costs and risk.
Types of Air Conditioning Systems

AC systems vary in design and application, and understanding the type you have helps determine the maintenance approach.
Central Air Systems
Central air systems are the most common choice for homes and light commercial buildings. They use a network of ducts to distribute cooled air evenly throughout the entire space, providing consistent temperature control and humidity management. Regular maintenance keeps airflow smooth and the system operating at its best.
Best For: Homes and light commercial buildings with existing ductwork, where even cooling across multiple rooms is a priority.
Ductless Mini-Splits
Ductless mini-splits consist of an indoor unit and an outdoor condenser, offering flexible installation without the need for existing ductwork. They provide zone-specific cooling, allowing different rooms to maintain independent temperatures, which helps reduce unnecessary energy use.
Best For: Spaces without existing ducts, room additions, or areas requiring precise temperature control in separate zones.
Heat Pumps
Heat pumps offer both cooling in summer and heating in winter by reversing the refrigeration cycle. They use less energy compared to traditional systems and can reduce reliance on separate heating systems, especially in moderate climates. Regular maintenance keeps refrigerant levels balanced and supports reliable operation in both modes.
Best For: Year-round comfort in moderate climates, where a single system can handle both heating and cooling.
Window and Portable Units
Window and portable air conditioners are self-contained systems that provide localized cooling. These units are easy to install and remove, but require frequent cleaning of filters and coils to maintain airflow and consistent performance.
Best For: Small rooms, temporary cooling solutions, or spaces where installing a permanent system is not feasible.
Each system type has unique vulnerabilities, so knowing your setup helps you prevent breakdowns and extend the system’s lifespan.
Key Strategies for Maintenance of Air Conditioning System
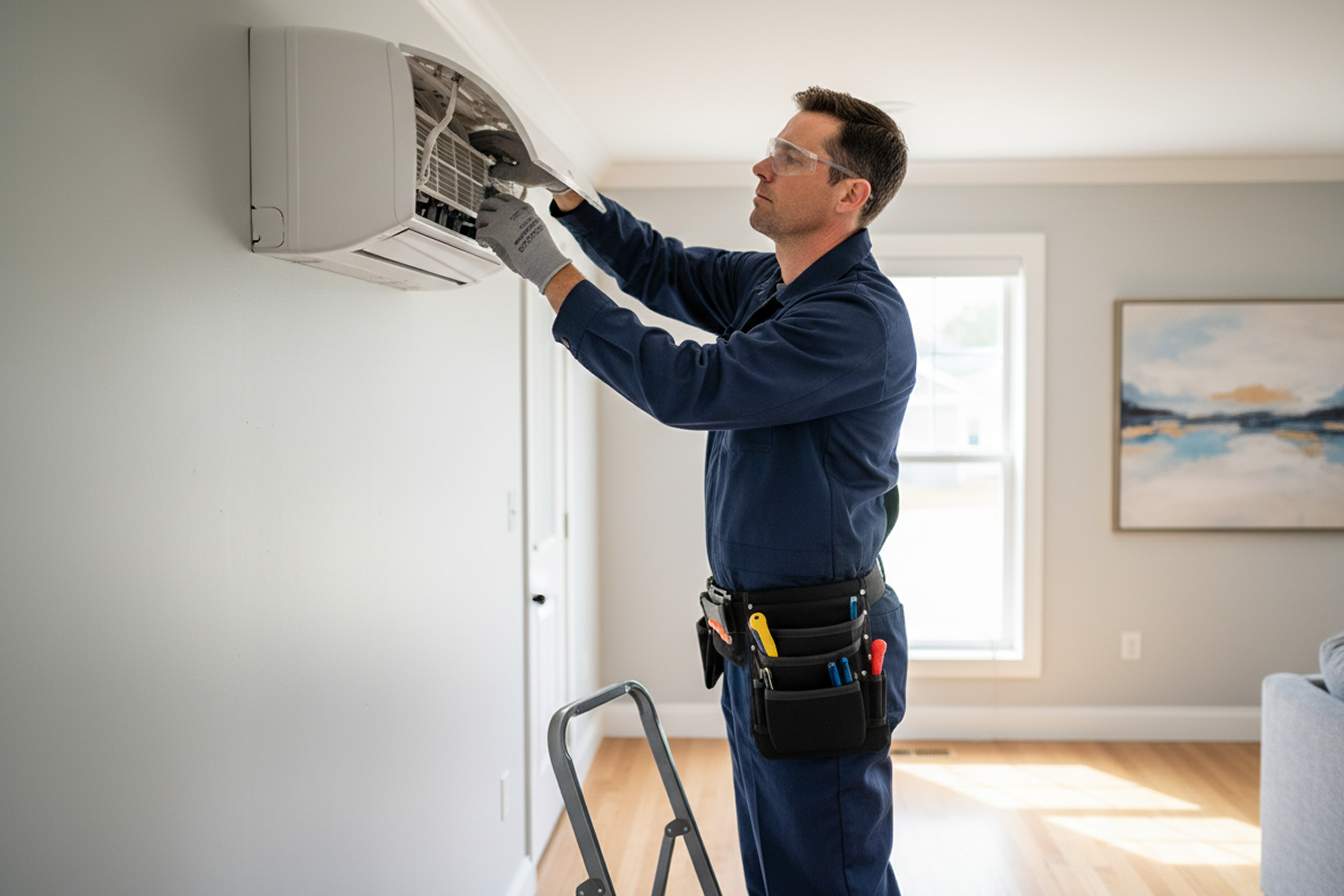

Effective AC maintenance combines regular checks, preventive actions, and professional inspections. Following a consistent plan ensures your system is reliable year-round.
Here’s how to keep your AC system running smoothly:
Schedule Regular Inspections
Seasonal inspections allow early detection of potential issues, keeping downtime minimal and energy costs in check.
Inspection checklist:
Evaluate refrigerant pressures according to manufacturer specifications
Check electrical connections for signs of wear or heat stress
Measure airflow across all vents for imbalances or obstructions.
Outcome: Helps reduce emergency repairs, prolongs component life, and keeps cooling consistent.
Change and Clean Air Filters
Filters are the first line of defense against dust and debris. Clogged filters reduce airflow, forcing the system to work harder and increasing wear and energy use.
Checklist for filters:
Replace or clean filters every 1–3 months based on usage and indoor air quality
Use filters appropriate for your system’s MERV rating
Inspect filters visually between changes for debris buildup
Outcome: Cleaner filters improve airflow, reduce energy use per unit of cooling, and protect internal components from unnecessary wear.
Clean Coils and Fins
Over time, evaporator and condenser coils accumulate dust and debris, reducing heat transfer efficiency and system performance.
Maintenance tasks:
Use approved coil cleaning solutions and follow manufacturer instructions
Straighten bent fins gently to maintain proper airflow
Inspect coils for corrosion, leaks, or physical damage
Performance measure: Effective heat transfer improves cooling output and lowers energy costs.
Verify Refrigerant Levels
Correct refrigerant charge ensures optimal cooling while minimizing stress on the compressor. Improper levels can reduce capacity and increase wear.
Professional checks should:
Measure refrigerant pressures using gauges per system design
Inspect for leaks in piping and connections
Adjust refrigerant charge to manufacturer specifications
Outcome: Maintains cooling performance without overloading equipment or increasing energy consumption.
Inspect Electrical Systems
Electrical issues, such as loose wiring or deteriorating parts, can lead to performance issues or safety risks if left unaddressed.
Routine checks include:
Tightening terminals and inspecting wiring insulation
Examining contactors, relays, and capacitors for wear
Measuring voltage and current for balanced operation
Impact: Maintaining electrical integrity reduces risk of outages, improves safety, and supports reliable operation.
Lubricate Moving Parts
Motors, fans, and bearings require proper lubrication to reduce friction. Dry or worn components use more power and wear faster.
Maintenance steps:
Apply the correct lubricant as specified by the manufacturer
Do not apply excess lubricant, as it can collect dust and cause buildup
Check moving parts for wear during lubrication
Benefit: Reduced friction leads to lower energy use and extends motor and fan lifespan.
Test Controls and Safety Devices
Thermostats, pressure cut-outs, and fan controls govern system operation. Checking their accuracy prevents unnecessary runtime and protects equipment.
Checks include:
Calibrate thermostat set points for accurate temperature control
Test high-pressure and safety cut-outs to confirm proper operation
Verify response times of system controls
Impact: Accurate controls reduce excessive cycling, prevent energy waste, and improve overall system reliability.
Maintain Condensate Drains
Clogged condensate lines or pans can lead to water damage, corrosion, and microbial growth. Regular maintenance helps avoid these issues.
Tasks include:
Clearing drain lines using manufacturer-approved methods
Inspecting drain pans for rust or blockages
Ensuring proper slope and drainage to prevent backups
Outcome: Functional drains reduce water damage risk and help maintain healthier indoor air quality.
These strategies combine DIY practices with professional support, helping your system run effectively, reduce downtime, and lower operating costs.
Common Air Conditioning Problems You Should Avoid
Even with good maintenance plans, certain issues repeatedly occur in systems that are not monitored or serviced. Awareness of common problems allows early detection and timely corrective action.
Here are common AC problems and how proper maintenance helps address them:
Poor Cooling Performance: Often caused by dirty filters, clogged coils, or low refrigerant. Regular maintenance resolves these issues early, before they affect comfort.
System Short Cycling: The AC turns on and off frequently, usually due to thermostat issues, restricted airflow, or oversized equipment. Timely inspections help identify root causes.
Strange Noises or Vibrations: These may indicate loose components, failing motors, or worn belts. Prompt professional attention limits further damage.
High Energy Bills: Reduced performance from unclean coils, leaky ducts, or improper refrigerant levels increases electricity consumption. Regular maintenance helps keep operating costs under control.
Water Leaks or Frozen Coils: Blocked condensate drains or low refrigerant can cause water damage or system freeze-ups. Periodic checks help avoid long-term damage.
Avoiding these common problems requires consistent attention and professional expertise to maintain system reliability and indoor comfort.
How Quality Comfort Solutions Can Support Your AC Maintenance?
Working with licensed HVAC professionals ensures that maintenance is thorough, safe, and aligned with best practices. Quality Comfort Solutions offers expertise and services designed to protect your investment and provide reliable indoor comfort.
Here’s how we can help you:
Scheduled Maintenance Contracts: Regular inspections and seasonal tune-ups that prevent costly breakdowns and extend system life.
Expert Repairs: Certified technicians quickly diagnose and fix mechanical, electrical, or refrigerant issues to minimize downtime.
Component Upgrades: Replacement or enhancement of key AC components for improved performance and energy savings.
24/7 Support: Rapid, around-the-clock response for emergencies, ensuring comfort and peace of mind any time of day.
Energy Efficiency Guidance: Recommendations on thermostat settings, system adjustments, and operational best practices to lower energy bills.
Licensed and Insured Team: All work is performed by certified professionals, ensuring compliance, safety, and consistent results.
Partnering with Quality Comfort Solutions provides peace of mind, reliable comfort, and improved energy performance for your home or light commercial facility.
Conclusion
Regular AC maintenance is a smart long-term decision that keeps your system running smoothly, lowers energy costs, and extends equipment life. By monitoring key components, performing routine checks, and addressing small issues early, homeowners and operations leaders can prevent costly breakdowns and maintain consistent comfort.
Balancing routine inspections and basic care with professional support helps you avoid common AC problems and reduces pressure on in‑house teams. An experienced HVAC partner like Quality Comfort Solutions can extend your internal capacity with structured planning, fast response, and technical know‑how that supports reliable cooling.
Contact us for a free estimate to schedule an AC maintenance plan tailored to your home or business needs.
FAQs
What are the daily or weekly maintenance steps for my air conditioner?
Check and clean air filters weekly to maintain airflow. Keep vents unobstructed and wipe dust from the indoor unit. Monitor thermostat settings and listen for unusual noises. Ensure the outdoor unit remains free of debris for proper heat exchange.
How do I clean the evaporator and condenser coils on my AC unit?
Turn off the power before cleaning. Gently loosen dust and buildup from the evaporator coils using a soft-bristle brush or a non-abrasive coil-cleaning solution. For condenser coils, gently hose off dirt and debris. Avoid bending fins, and consider professional cleaning for deep buildup.
When should I schedule professional AC servicing, and how often?
Plan for professional maintenance at least once each year, preferably before the summer season begins.. For heavily used systems, twice-yearly servicing helps maintain efficiency, detect issues early, and extend system lifespan while preventing unexpected breakdowns.
What are the signs that my AC needs refrigerant recharge or repair?
Common signs include weak cooling, warm air from vents, ice buildup on coils, hissing sounds, or rising energy bills. If your AC runs longer without cooling effectively, it likely needs refrigerant inspection or repair by a licensed technician.
What role does room insulation and sealing play in AC maintenance?
Proper insulation and sealing reduce heat gain, allowing your AC to cool efficiently. Sealed doors, windows, and insulated walls minimize air leakage, lower energy consumption, reduce strain on components, and help maintain consistent indoor temperatures.