Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) controls are the brains behind modern systems. They regulate how and when your system heats, cools, ventilates, and manages indoor conditions, ensuring your space stays comfortable without wasting energy.
The HVAC controls market is rapidly expanding, with the global market size projected to reach $39.7 billion by 2030.
From simple thermostats to advanced building automation systems, HVAC controls determine how efficiently your system responds to changing temperatures, occupancy levels, and air quality needs.
As sustainability standards become stricter and energy costs rise, effective control systems help eliminate temperature swings, reduce unnecessary system runtimes, and maintain healthier indoor air by managing humidity and ventilation more precisely.
Whether in a home or a commercial building, well‑designed HVAC controls play a critical role in improving comfort, lowering operating costs, and extending equipment lifespan, making them a key investment for smarter, greener buildings.
In this guide, you’ll learn what HVAC controls are, how they work, and the different types available today. We’ll also explore their key benefits, advanced features, common applications, and best practices.
Key Takeaways
HVAC controls manage temperature, airflow, humidity, and ventilation, acting as the system’s brain to deliver comfort, efficiency, and indoor performance.
Modern HVAC control systems use thermostats, sensors, controllers, and actuators to sense conditions, decide actions, and adjust equipment automatically and efficiently.
Manual, programmable, smart, and building automation controls offer increasing automation levels, helping homes and businesses balance comfort, efficiency, and costs.
Advanced features like zoning, demand-controlled ventilation, and variable frequency drives reduce energy waste while improving indoor comfort and system longevity.
Choosing the right HVAC controls and following best practices ensures lower bills, healthier indoor air, and longer-lasting cooling equipment performance.
What Are HVAC Controls?
HVAC controls are the systems and devices that manage how heating, cooling, and ventilation equipment operate within a building. Their primary role is to maintain comfortable indoor conditions, such as temperature, humidity, airflow, and air quality, while minimizing energy waste.
In simple terms, HVAC controls decide when the system runs, how it responds, and how efficiently it operates.
These control systems rely on several key components working together to monitor conditions and adjust system performance:
Thermostats: The main user interface for setting temperature preferences
Sensors: Measure temperature, humidity, occupancy, and indoor air quality in real time
Controllers: Process sensor data and determine appropriate system responses
Actuators and dampers: Execute commands by adjusting airflow, valves, and equipment operation
As HVAC technology has advanced, automated control systems have become the standard in both residential and commercial settings. They deliver more consistent comfort, improve energy efficiency, and ensure HVAC systems operate smoothly across changing conditions, making them an essential part of modern HVAC design.
How HVAC Controls Work

HVAC controls operate through a coordinated process that continuously monitors indoor conditions and adjusts system performance to meet comfort and efficiency goals. Instead of simply turning equipment on or off, modern control systems rely on real-time feedback, logic-based decision-making, and mechanical responses to maintain stable indoor environments.
At a high level, HVAC controls follow a simple cycle: sense → decide → act. Sensors collect data, controllers interpret that information, and mechanical components carry out the required adjustments.
Thermostatic Control
The thermostat serves as the primary control point between occupants and the HVAC system. It allows users to set desired temperature ranges and communicates those preferences to the control system.
Common thermostat types include:
Manual thermostats: Require physical adjustments and provide basic on/off control
Programmable thermostats: Allow scheduled temperature changes based on time of day
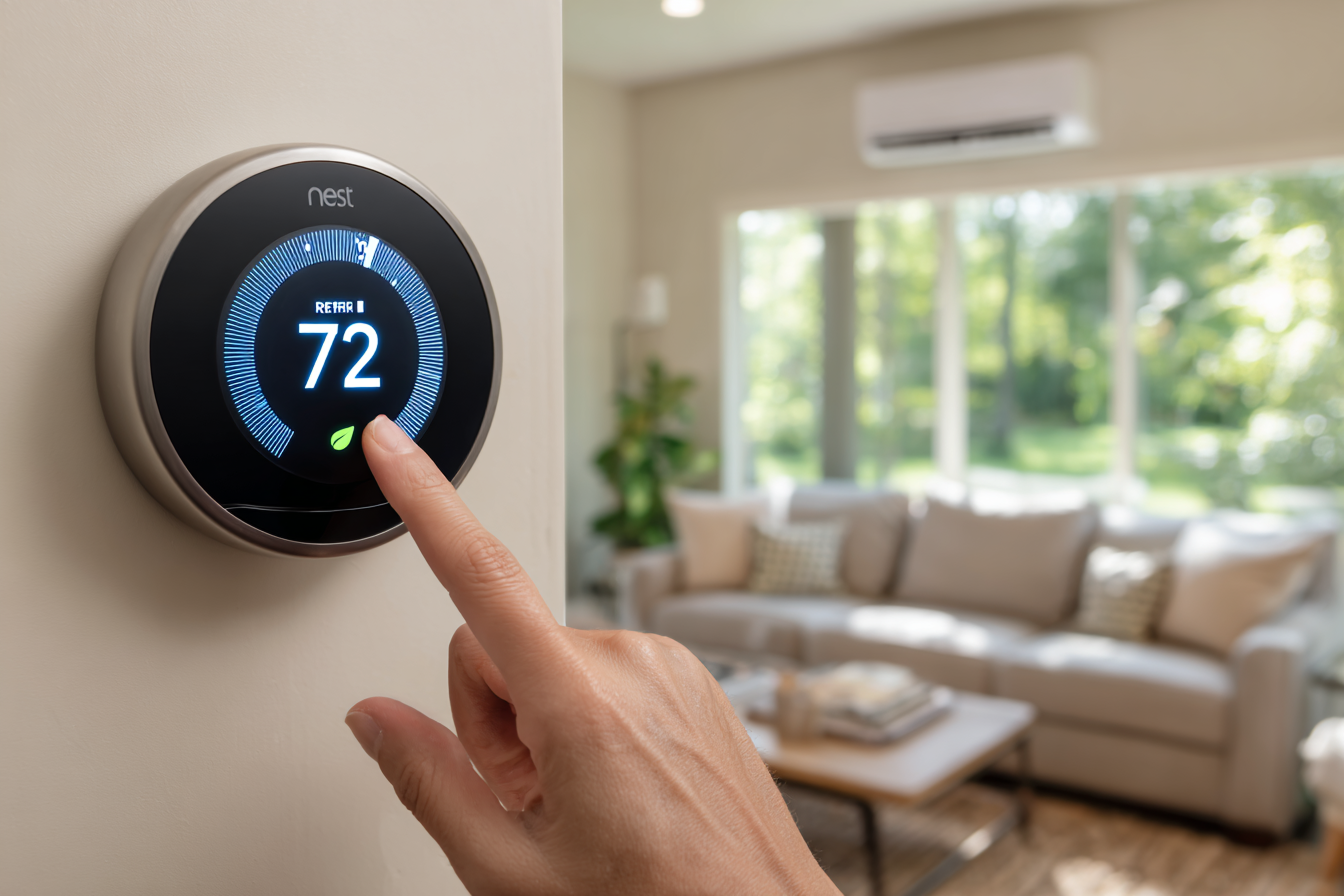
Smart thermostats: Learn user behavior, enable remote access, and optimize energy use automatically
By maintaining set temperature thresholds, thermostatic controls help prevent overconditioning while ensuring consistent comfort.
Sensors and Feedback Loops
Sensors provide the data that HVAC controls rely on to make accurate decisions. They continuously measure environmental conditions and send that information back to the controller.
Key sensor types include:
Temperature sensors for heating and cooling accuracy
Humidity sensors to manage moisture levels and comfort
Occupancy sensors to adjust operation based on space usage
Air quality sensors that monitor pollutants and ventilation needs
This ongoing feedback creates a closed-loop system, allowing HVAC controls to adapt in real time as conditions change.
Actuators and Mechanical Controls
Once a decision is made, actuators carry out the physical actions required to adjust the HVAC system. These components convert control signals into mechanical movement.
Typical actuators and controls include:
Motorized dampers that regulate airflow
Valves that control heating or cooling fluid flow
Fan and compressor controls that adjust system output
Together, these components ensure air and energy are delivered precisely where and when they’re needed.
Zoning and Multi-Zone Control
Zoning systems divide a building into separate areas, each with its own temperature settings and controls. This allows HVAC systems to respond to different comfort needs within the same structure.
Benefits of zoning control include:
Targeted temperature management for individual spaces
Reduced energy waste in unoccupied zones
Improved comfort by eliminating hot and cold spots
By coordinating sensors, thermostats, and dampers, zoning systems deliver more personalized comfort while improving overall system efficiency.
Types of HVAC Control Systems
HVAC control systems vary in complexity, from basic manual adjustments to fully automated, data-driven platforms. Choosing the right type depends on the size of the building, comfort expectations, and energy efficiency goals. Understanding the differences helps homeowners and facility managers select a system that balances performance and cost.
Manual HVAC Controls
Manual controls are the simplest form of HVAC management. They rely entirely on user input and provide limited automation.
Key characteristics include:
Basic thermostats with on/off or temperature dial adjustments
No scheduling or learning capabilities
Lower upfront cost but less efficient operation
Manual controls are best suited for small spaces or systems with minimal comfort variability.
Programmable HVAC Controls
Programmable controls add scheduling functionality, allowing temperature changes to be set in advance.
Common features include:
Daily or weekly temperature schedules
Reduced energy use during unoccupied hours
Improved consistency compared to manual controls
These systems are ideal for homeowners or businesses with predictable routines who want better efficiency without advanced automation.
Smart HVAC Controls
Smart controls use sensors, connectivity, and data analysis to optimize HVAC performance automatically.
Typical capabilities include:
Remote access via smartphone apps
Adaptive learning based on usage patterns
Integration with voice assistants and smart home systems
Energy usage tracking and alerts
Smart HVAC controls provide enhanced comfort and efficiency, making them increasingly popular in modern residential and light commercial applications.
Building Automation Systems (BAS) and Direct Digital Control (DDC)
BAS and DDC systems are designed for large commercial and institutional buildings where centralized control is essential.
Key advantages include:
Centralized monitoring and control of multiple HVAC systems
Advanced zoning and scheduling across large spaces
Data analytics for performance optimization and maintenance planning
These advanced control systems help large facilities reduce operating costs, improve reliability, and maintain consistent indoor conditions at scale.
Key Benefits of HVAC Controls
HVAC controls do more than regulate temperature. They directly impact energy usage, comfort levels, indoor air quality, and system longevity. Whether in residential or commercial settings, the right control system can significantly improve overall HVAC performance while reducing operational costs.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
One of the most significant advantages of HVAC controls is improved energy efficiency. By operating equipment only when needed and at optimal levels, controls help reduce unnecessary energy consumption.
Key efficiency benefits include:
Targeted heating and cooling based on real-time conditions
Scheduled operation to avoid conditioning unused spaces
Reduced system runtime and energy waste
These efficiencies translate into lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint over time.
Enhanced Comfort and Indoor Air Quality
HVAC controls maintain consistent indoor conditions by minimizing temperature fluctuations and balancing airflow throughout a space.
Comfort and air quality improvements include:
Even temperatures without hot or cold spots
Better humidity control for healthier indoor environments
Optimized ventilation to support fresh air circulation
Together, these features create a more comfortable and healthier living or working environment.
Remote Access and Smart Features
Modern HVAC control systems offer advanced connectivity that allows users to monitor and adjust settings from anywhere.
Popular smart features include:
Mobile app control and remote adjustments
Voice commands and smart home integration
Geofencing and automated comfort settings
Energy usage insights and performance alerts
These features provide convenience while helping users stay informed about system efficiency.
Extended System Lifespan
By optimizing how often and how hard HVAC equipment operates, control systems help reduce mechanical stress and wear.
Long-term system benefits include:
Fewer short cycling events
Smoother operation and balanced load distribution
Early issue detection through alerts and diagnostics
As a result, HVAC systems last longer, require fewer repairs, and deliver more reliable performance throughout their lifespan.
Advanced HVAC Control Features

Advanced HVAC control features take system performance beyond basic temperature regulation. These technologies use real-time data, automation, and system integration to maximize efficiency, improve comfort, and support smarter building management, especially in modern homes and commercial facilities.
Demand-Controlled Ventilation (DCV)
Demand-controlled ventilation adjusts fresh air intake based on actual occupancy and air quality rather than fixed schedules.
Key advantages include:
Reduced energy use by limiting unnecessary ventilation
Improved indoor air quality during high-occupancy periods
Better compliance with modern ventilation standards
DCV is especially valuable in spaces with fluctuating occupancy, such as offices and conference areas.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs)
Variable frequency drives control motor speed instead of operating motors at full capacity all the time.
Benefits of VFDs include:
Lower energy consumption by matching output to demand
Smoother motor operation with reduced wear and noise
Greater control over fans, pumps, and compressors
By adjusting motor speed dynamically, VFDs significantly enhance overall HVAC efficiency.
Integration with Building Automation Systems
Advanced HVAC controls often integrate with building automation systems (BAS) to centralize monitoring and management.
Integration benefits include:
Unified control of HVAC, lighting, and other building systems
Centralized data collection and performance analytics
Faster issue detection and streamlined maintenance
This level of integration allows facility managers to optimize building operations from a single platform while improving reliability and energy performance.
Common Applications of HVAC Controls
HVAC controls are used across a wide range of settings, from single-family homes to large commercial buildings. While the core principles remain the same, the complexity and features of HVAC control systems vary depending on application size, occupancy patterns, and performance requirements.
Residential HVAC Controls
In residential settings, HVAC controls focus on comfort, convenience, and energy savings. Homeowners benefit from intuitive systems that adapt to daily routines and changing weather conditions.
Common residential control applications include:
Thermostats for basic temperature regulation
Zoning systems to control different areas of the home independently
Smart controls with mobile access and automated adjustments
These solutions help reduce energy waste while maintaining consistent comfort throughout the home.
Commercial HVAC Controls
Commercial HVAC controls are designed to manage larger spaces with diverse occupancy needs and higher system demands. Centralized control and automation are critical in these environments.
Typical commercial applications include:
BAS and DDC
Advanced zoning for offices, retail spaces, and facilities
Energy monitoring and performance analytics
By coordinating multiple HVAC systems from a single platform, commercial controls improve efficiency, enhance comfort, and simplify long-term facility management.
Choosing the Right HVAC Control System
Selecting the right HVAC control system is essential for achieving the best balance between comfort, efficiency, and cost. The ideal solution depends on your space, usage patterns, and long-term performance goals.
Key considerations when choosing an HVAC control system include:
Building size and layout: Larger or multi-level spaces often require advanced or zoned controls
Occupancy patterns: Variable schedules benefit from programmable or smart systems
Budget and energy goals: Higher upfront costs can deliver long-term energy savings
System compatibility: Controls must match existing HVAC equipment
Professional installation and calibration are just as important as selecting the right technology. Proper setup ensures sensors are placed correctly, controls are configured accurately, and the system operates at peak efficiency. Working with an HVAC professional helps avoid performance issues and ensures your control system delivers consistent, reliable results.
Best Practices for HVAC Controls
Even the most advanced HVAC control system requires proper setup and ongoing management to perform effectively. Following best practices helps maintain comfort, improve efficiency, and prevent long-term performance issues.
Key best practices for optimal HVAC control performance include:
Regular schedule reviews: Update temperature schedules to reflect current usage patterns
Proper sensor placement: Ensure sensors are installed away from heat sources, drafts, or direct sunlight
Routine calibration: Keep sensors and thermostats accurately aligned with actual conditions
Firmware and software updates: Maintain smart controls and automation systems with the latest updates
Performance monitoring: Review energy reports and alerts to identify inefficiencies early
By staying proactive with maintenance and monitoring, HVAC controls can consistently deliver energy savings, reliable comfort, and extended system lifespan.
Why Choose Quality Comfort Solutions for HVAC Control Systems
Upgrading or optimizing HVAC controls requires more than just new technology. It requires expert evaluation, precise installation, and ongoing support. Quality Comfort Solutions provides professional HVAC control solutions designed to improve comfort, efficiency, and system reliability for residential and commercial properties.
Their team takes a customized approach, assessing your existing HVAC setup and recommending control systems that align with your space, usage patterns, and energy goals.
What sets Quality Comfort Solutions apart:
Expert system assessments to identify control inefficiencies
Smart thermostat and zoning solutions tailored to your needs
Professional installation and calibration for accurate performance
Energy-efficiency optimization to reduce operating costs
Support for residential and commercial HVAC systems
By combining industry expertise with modern HVAC control technologies, Quality Comfort Solutions helps ensure your system operates efficiently, delivers consistent comfort, and performs reliably year-round. Schedule a call today to get started.
Conclusion
HVAC controls are the backbone of modern heating, cooling, and ventilation systems, ensuring comfort, energy efficiency, and reliable performance. From simple manual thermostats to advanced smart controls and building automation systems, the right control solution can make a significant difference in how your HVAC system operates.
By understanding how controls work, exploring the types available, and following best practices, homeowners and facility managers can optimize comfort, lower energy costs, and extend the lifespan of their equipment.
Ready to upgrade your HVAC controls for better comfort and efficiency?
Trust the experts at Quality Comfort Solutions for professional guidance, system upgrades, and precision installation tailored to your home or business. Schedule your consultation today.
FAQs
1. What does HVAC control?
HVAC controls regulate indoor temperature, humidity, airflow, and ventilation by managing heating, cooling, and air circulation equipment to maintain comfort, efficiency, and healthy indoor air quality.
2. What are the 4 types of automatic controls in HVAC?
The four automatic HVAC controls are thermostatic controls, pressure controls, humidity controls, and flow controls, each automatically adjusting system operation based on changing environmental conditions.
3. Are HVAC controls AC or DC?
HVAC controls can use both AC and DC power; control circuits typically operate on low-voltage AC, while modern electronic and smart components often rely on DC power.
4. What is control voltage?
Control voltage is the low-voltage power, commonly 24 volts, used to safely operate HVAC control circuits, thermostats, relays, and sensors without powering high-voltage equipment directly.
5. Does HVAC have a breaker?
Yes, HVAC systems have dedicated circuit breakers that protect equipment from electrical overloads, short circuits, and faults by shutting off power during unsafe electrical conditions.
6. Do HVAC systems have fuses?
Yes, many HVAC systems include fuses within control boards or disconnects to protect low-voltage circuits and components from electrical surges or short-circuit damage.


