Homeowners today are looking for heating systems that balance comfort, efficiency, and cost, especially in regions with unpredictable winter temperatures. That’s why heat pumps with gas furnace dual fuel systems are gaining attention as a smart, flexible solution.
The shift toward electric heating technology is already underway. In the U.S. in 2025, heat pumps have outsold gas furnaces by about 25%, reflecting growing homeowner interest in high-efficiency systems and the transition away from fossil fuel dependence.
Despite this surge in new installations, only a small portion of U.S. homes currently use heat pumps, estimated at roughly 14% of households, highlighting the large potential for future adoption, especially when paired with existing gas infrastructure.
In this guide, we’ll explain how dual fuel systems work, their benefits and drawbacks, and when they make the most sense for local climates. If you’re considering a heating upgrade that delivers efficiency without compromising comfort, understanding dual fuel systems is an essential first step.
Key Takeaways:
Dual fuel systems combine an electric heat pump with a gas furnace to automatically optimize efficiency, comfort, and performance year-round.
Heat pumps provide efficient heating in mild weather, while gas furnaces deliver powerful, reliable warmth during freezing temperatures winter conditions.
Automatic switching uses a thermostat balance point to choose the most cost-effective heating source based on outdoor temperature and efficiency.
Dual fuel systems lower energy bills, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce emissions by limiting gas use while maximizing electric heat.
Dual fuel HVAC works best in mixed cold climates with gas access, offering comfort, flexibility, and savings for homeowners year-round.
What Is a Dual Fuel System?
A dual fuel system is a high-efficiency Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) solution that combines an electric heat pump with a gas furnace to deliver consistent comfort across varying weather conditions.
Instead of relying on one heating source all year, the system automatically switches between electricity and natural gas to maximize efficiency and performance. The heat pump handles heating during mild to moderately cold weather, while the gas furnace takes over when temperatures drop significantly.
This “best of both worlds” approach helps homeowners:
Lower energy bills
Reduce unnecessary wear on equipment
Maintain consistent indoor comfort
How Dual Fuel Systems Work?

A heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system is designed to automatically select the most efficient heating method based on outdoor temperatures and comfort demand. Rather than running one system year-round, it intelligently alternates between the heat pump and the gas furnace to optimize performance, energy use, and comfort.
Below is a breakdown of how each component works and how the system decides when to switch.
Heat Pump Operation
The heat pump serves as the primary heating source during mild to moderately cold weather.
Instead of generating heat, a heat pump moves heat from the outdoor air into your home using electricity. Even when it feels cold outside, there is still usable heat energy in the air that the system can extract.
Key characteristics of heat pump operation include:
Highly energy-efficient heating in temperatures above roughly 30–40°F
Lower operating costs compared to gas heat during shoulder seasons
Even, consistent indoor temperatures without intense heat bursts
Dual functionality, providing air conditioning in summer as well
Because of this efficiency, the heat pump handles the majority of heating needs during fall, early winter, and spring in climates like Westchester County and Yonkers.
Gas Furnace Operation
When outdoor temperatures drop below the heat pump’s efficient operating range, the gas furnace automatically takes over.
Gas furnaces generate heat by burning natural gas, allowing them to deliver powerful and immediate warmth regardless of outdoor conditions. This makes them ideal for freezing temperatures and extended cold snaps common in the Northeast.
The gas furnace is typically used when:
Outdoor temperatures fall below the system’s balance point
Rapid temperature recovery is needed after a setback
Extreme cold reduces heat pump efficiency
By reserving gas heat for when it’s truly needed, the system avoids unnecessary fuel usage while maintaining comfort.
Automatic Switching Logic (Balance Point)
The defining feature of a dual fuel system is its automatic switching capability.
A smart thermostat or control system continuously evaluates:
Outdoor temperature
Indoor comfort demand
Energy efficiency and utility costs
Based on this data, the system determines the balance point. The temperature at which it becomes more efficient to switch from electric heat pump operation to gas furnace heating.
Key advantages of automatic switching include:
No manual intervention required from the homeowner
Optimized energy use in changing weather conditions
Consistent comfort without performance drops
This intelligent control allows dual fuel HVAC systems to adapt seamlessly to fluctuating winter temperatures, making them especially effective in mixed-climate regions.
Key Components of a Dual Fuel System
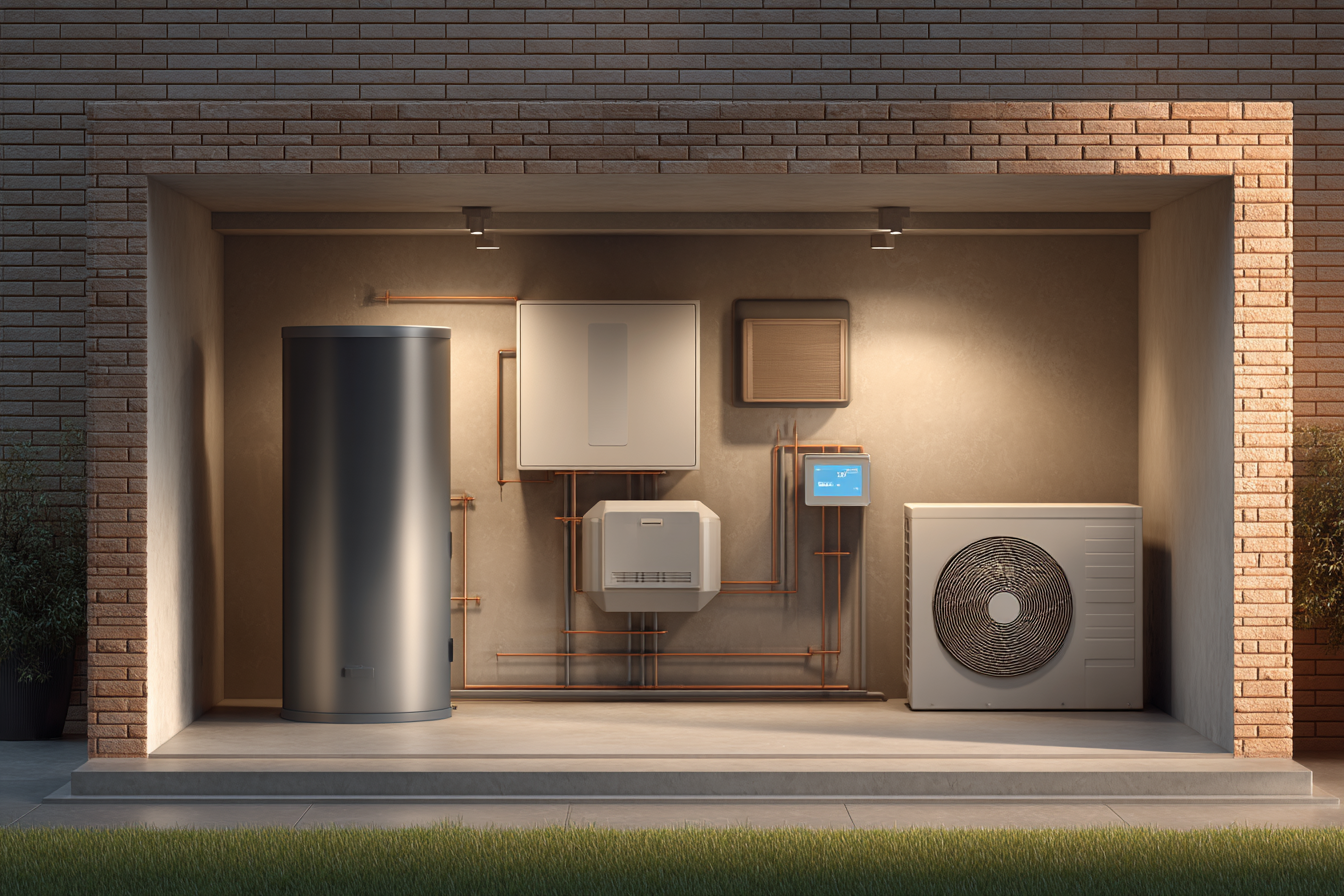
A heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system relies on several integrated components working together to deliver efficient, reliable comfort throughout the year. Each part plays a specific role in heating, cooling, and automatically switching between fuel sources.
Understanding these components helps homeowners see why proper system design and professional installation are so important.
Outdoor Heat Pump Unit
The outdoor unit is responsible for both heating and cooling the home.
It includes key parts such as the compressor, outdoor coil, and fan, which allow the system to extract heat from the air in winter and release heat outdoors in summer.
Key functions include:
Providing energy-efficient heating during mild to moderate cold
Acting as the air conditioner during warm months
Reducing overall reliance on gas heat
Because the heat pump operates most of the year, efficiency ratings like Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) play a major role in long-term energy savings.
Indoor Gas Furnace
The gas furnace serves as the backup and cold-weather heating source.
Located indoors, the furnace uses a burner and heat exchanger to generate powerful heat when outdoor temperatures drop too low for efficient heat pump operation.
Its primary roles include:
Delivering fast, consistent heat in freezing conditions
Maintaining comfort during extended cold snaps
Supporting the heat pump when demand is high
This combination ensures dependable warmth even during Northeast winter extremes.
Smart Thermostat or Control System
The thermostat or control board is the brain of the dual fuel system.
It continuously monitors temperature conditions and determines when to switch between the heat pump and gas furnace for optimal efficiency and comfort.
Key responsibilities include:
Managing the system’s balance point
Automating fuel switching without homeowner input
Optimizing performance based on outdoor conditions
Advanced smart thermostats can further improve energy efficiency by adjusting operation based on usage patterns.
Ductwork and Air Distribution System
The ductwork delivers conditioned air throughout the home.
Properly sealed and sized ducts are essential to ensure:
Even airflow to all rooms
Reduced energy loss
Consistent indoor temperatures
Poor duct design can reduce the benefits of a dual fuel system, which is why inspections and upgrades are often recommended during installation.
Benefits of Dual Fuel Systems

Below are the key advantages that make dual fuel HVAC systems a popular choice.
Energy Efficiency & Lower Operating Costs
One of the biggest benefits of a dual fuel system is its ability to use the most efficient heating source at any given time.
Heat pumps provide low-cost electric heating during mild weather
Gas furnaces are reserved for colder temperatures when the electric efficiency drops
Automatic switching prevents wasted energy and unnecessary fuel use
This optimized operation can lead to lower monthly utility bills, particularly in regions with fluctuating winter temperatures.
Year-Round Comfort
Dual fuel systems are designed to maintain comfort no matter the season.
Homeowners benefit from:
Consistent indoor temperatures during fall and winter
Strong, reliable heat during freezing conditions
Efficient air conditioning during the summer months
The system adapts to temperature changes without sacrificing comfort or performance.
Extended Equipment Life
Because heating duties are shared between two systems, neither the heat pump nor the furnace has to do all the work.
This balanced workload helps:
Reduce wear and tear on individual components
Lower the risk of breakdowns during peak seasons
Extend the overall lifespan of the HVAC system
Over time, this can translate into fewer repairs and better long-term value.
Reduced Environmental Impact
Dual fuel systems can help homeowners lower their carbon footprint.
The heat pump reduces reliance on fossil fuels during most of the heating season
Less gas consumption means fewer greenhouse gas emissions
Efficient electric operation supports cleaner energy goals
For homeowners looking to improve efficiency while still needing dependable cold-weather heat, dual fuel systems offer a practical middle ground.
Drawbacks and Considerations
While a heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system offers many advantages, it’s important to understand the potential drawbacks before deciding if it’s the right solution for your home. Like any advanced HVAC setup, dual fuel systems come with specific considerations related to cost, complexity, and infrastructure.
Higher Upfront Installation Costs
Dual fuel systems typically cost more to install than single-system options.
Requires both a heat pump and a gas furnace
Involves additional controls and setup
May include ductwork or electrical upgrades
Although operating costs are often lower over time, the initial investment can be higher.
More Complex System Design
Because dual fuel systems rely on two heating technologies, installation and configuration must be done correctly.
Considerations include:
Proper sizing of both the heat pump and furnace
Accurate balance point setup
Compatibility between equipment and thermostat
Improper installation can reduce efficiency and negate system benefits.
Dependence on Natural Gas Availability
A dual-fuel HVAC system requires access to a reliable natural gas supply.
Not ideal for homes without gas infrastructure
Gas availability and pricing can vary by location
Backup heat depends on continued gas service
For all-electric homes, a standalone heat pump may be more practical.
Thermostat and Control Requirements
To function properly, dual fuel systems often require advanced thermostats or control boards.
The balance point must be programmed correctly
Incorrect settings can increase energy costs
Older thermostats may not be compatible
Professional configuration is strongly recommended to ensure optimal performance.
When Dual Fuel Systems Make Sense

Below are the scenarios where dual-fuel HVAC systems make the most sense.
Homes in Mixed or Cold Climates
Dual fuel systems perform best in regions with cold winters but fluctuating temperatures, such as Yonkers and Westchester County, NY.
They are ideal when:
Winters include both mild days and freezing nights
Temperatures frequently hover around the heat pump’s efficiency range
Extended deep-freeze conditions are possible but not constant
This allows the heat pump to handle most heating while the gas furnace provides dependable backup.
Properties with Existing Natural Gas Infrastructure
Homes that already have natural gas service are strong candidates for dual fuel systems.
Benefits include:
Lower installation complexity compared to adding gas later
Ability to use high-efficiency gas heat when needed
Reduced reliance on electric resistance backup heating
This makes dual fuel an efficient upgrade path for many older homes.
Homeowners Focused on Lower Heating Costs
Dual fuel systems are well-suited for households aiming to reduce winter energy expenses.
They work well when:
Electricity is cost-effective during shoulder seasons
Gas prices are competitive for deep-winter heating
Homeowners want to avoid overusing a single energy source
By switching automatically, the system helps control heating costs throughout the season.
Comfort-Driven Households
For homeowners who prioritize comfort without compromise, dual fuel systems offer:
Faster heating response during extreme cold
Stable indoor temperatures during weather swings
Peace of mind knowing backup heat is always available
This combination makes dual-fuel HVAC systems a reliable choice for families in colder regions.
Installation and Best Practices
Installing a heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system requires careful planning, professional expertise, and proper configuration to ensure maximum efficiency, comfort, and longevity. Following best practices during installation can prevent common issues and optimize performance year-round.
Proper Thermostat Configuration
The thermostat is the “brain” of a dual fuel system, controlling when the heat pump or gas furnace operates. Proper setup is essential:
Set the balance point accurately for your local climate to switch efficiently between electric and gas heat
Use a smart or programmable thermostat to optimize performance and reduce energy costs
Regularly monitor system performance to ensure the switching logic is functioning correctly
A correctly configured thermostat ensures the system automatically chooses the most efficient heating source without manual intervention.
Professional Design & Installation
Because dual fuel systems combine two heating technologies, professional installation is highly recommended:
Licensed HVAC contractors ensure proper sizing and compatibility of heat pump and furnace units
Proper ductwork inspection guarantees efficient airflow and prevents energy loss
Expert installation protects manufacturer warranties and reduces the risk of operational issues
System testing after installation ensures the heat pump, gas furnace, and thermostat work seamlessly together
Investing in professional installation pays off with better energy efficiency, fewer repairs, and longer equipment life.
Additional Considerations for Longevity
Schedule annual maintenance for both the heat pump and the furnace
Ensure outdoor unit clearance and proper airflow around the heat pump
Monitor gas supply and connections for safety and reliability
Following these best practices helps homeowners enjoy the full benefits of a dual fuel HVAC system for many years.
Comparison: Dual Fuel vs Standalone Heat Pump and Furnace
When considering a heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system, it’s important to understand how it compares to standalone heat pumps or standalone gas furnaces. Each option has unique advantages, but dual fuel systems offer a combination of efficiency and reliability that single systems may lack.
System Type | Efficiency in Mild Weather | Efficiency in Extreme Cold |
|---|---|---|
Standalone Heat Pump | High – uses electricity efficiently | Low – may require electric resistance backup, increasing costs |
Standalone Gas Furnace | Moderate – burns fuel even when mild heat would suffice | High – reliable heat in extreme cold |
Dual Fuel System | High – heat pump operates in mild/moderate temperatures | High – gas furnace takes over in extreme cold |
Why Choose Quality Comfort Solutions for Your Dual Fuel System Needs
When it comes to upgrading or installing a heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system, having a trusted local HVAC partner makes all the difference. Quality Comfort Solutions is a licensed and insured HVAC contractor serving Yonkers and Westchester County, NY, offering personalized heating and cooling services tailored to your home’s needs.
Here’s how they support homeowners throughout the entire dual fuel process:
Comprehensive HVAC Services: Quality Comfort Solutions handles everything from heat pump installations and gas furnace setups to seasonal maintenance and emergency repairs, ensuring your system performs reliably all year.
Expert Installation & Support: Their certified team brings years of experience to every project, ensuring proper system sizing, thermostat setup, and seamless integration between your heat pump and furnace.
Prompt, Dependable Service: With 24/7 support and quick response times, they’re committed to keeping your home comfortable, even during unexpected breakdowns or cold snaps.
Seasonal Maintenance Plans: Regular tune-ups help maximize efficiency, prevent costly breakdowns, and extend the life of both your heat pump and gas furnace, critical for getting the most out of a dual fuel system.
Whether you’re ready for a system upgrade or need expert advice on how dual fuel solutions can benefit your home, Quality Comfort Solutions offers experience local homeowners rely on. Book a call today.
Conclusion
A heat pump with a gas furnace dual fuel system offers homeowners the perfect balance of energy efficiency, reliable cold-weather performance, and year-round comfort. By automatically switching between electric heat pumps and gas furnaces, these systems optimize energy use, reduce heating costs, and maintain consistent indoor temperatures.
Dual fuel systems are ideal for homes with existing natural gas infrastructure, households looking to lower utility bills, and anyone seeking comfortable, efficient heating without compromise. While the upfront investment and installation complexity are higher than single-system setups, the long-term benefits, including extended equipment life and environmental advantages, often outweigh the initial costs.
If you’re considering upgrading your home’s heating system, consulting a professional HVAC provider is key. At Quality Comfort Solutions, our team can assess your home, determine the right dual fuel system, and handle expert installation to ensure optimal performance.
Take the next step toward efficient, reliable home heating. Contact Quality Comfort Solutions today for a dual fuel system consultation.
FAQs
1. Can a heat pump and furnace work at the same time?
In a dual fuel system, the heat pump and furnace do not run simultaneously; the system automatically switches between them based on temperature, efficiency, and thermostat control logic.
2. Which is more efficient, a heat pump or a gas furnace?
A heat pump is more efficient in mild weather because it moves heat, not creates it, while a gas furnace is more efficient during extremely cold temperatures.
3. What is the lifespan of a gas absorption heat pump?
A gas absorption heat pump typically lasts 20 to 25 years with proper maintenance, often longer than standard electric heat pumps or conventional gas furnaces.
4. How does a heat pump with gas backup work?
A heat pump with gas backup uses electric heat during mild temperatures, then automatically switches to the gas furnace when outdoor conditions drop below the system’s efficiency balance point.
5. Do heat pumps lose efficiency with age?
Yes, heat pumps gradually lose efficiency due to normal wear, refrigerant issues, and component aging, but regular maintenance can significantly slow performance decline over time.
6. Do I need both a furnace and a heat pump?
You need both only if you live in a mixed or cold climate, have gas access, and want efficient heating in mild weather with reliable backup heat.


